Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jul 29, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 29 July 2020
US equity markets closed higher, while APAC and European markets closed mixed for the second consecutive day. The conclusion of the two-day FOMC meeting gave a further boost to US equities and credit late in the day, while also driving the US dollar lower. iTraxx and CDX indices closed tighter across IG/high yield and oil also closed higher on the day. All eyes will be on tomorrow's 8:30am EST US weekly claims for unemployment insurance to see if the recent uptick in jobless claims continues in the wake of the increasing number of business restrictions aimed at slowing the spread of COVID-19.
Americas
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) concluded its scheduled 2-day policy meeting this afternoon. The statement released at the conclusion of the meeting indicated, as we expected, that the FOMC held the target for the federal funds rate at its current setting of a range of 0% to ¼%. Net investment in Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities (MBS) will continue at least at their current paces. Today's statement was consistent with IHS Markit's forecast. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny and Kathleen Navin)
- The Federal Reserve has warned that the fate of the world's largest economy would "depend significantly on the course of the virus" as the US central bank extended measures to deal with the risk of an international shortage of dollars. In an indication of concerns that the pandemic could stir fresh trouble in international financial markets in future, such as the dollar shortages that occurred early in the pandemic, the Fed said it would extend emergency swap lines with some central banks until the end of the first quarter of 2021, as well as a temporary repurchase facility for international monetary authorities to swap Treasuries for dollars. (FT)
- US equity markets closed higher today, with the Fed providing a strong tailwind in the afternoon; Russell 2000 +2.1%, Nasdaq +1.4%, S&P 500 +1.2%, and DJIA +0.6%. The 2:00pm EST post-FOMC meeting announcement and Fed Chairman Powell's press conference 30 minutes created positive momentum in the equity markets, which retreated at 3:00pm EST and then surged to the intraday high after 3:30pm EST.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed flat/0.58% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/1.25% yield.
- DXY US dollar index closed at -0.5%/93.26, with a brief rally from the lows occurring at the conclusion of Fed Chairman Powell's press conference.
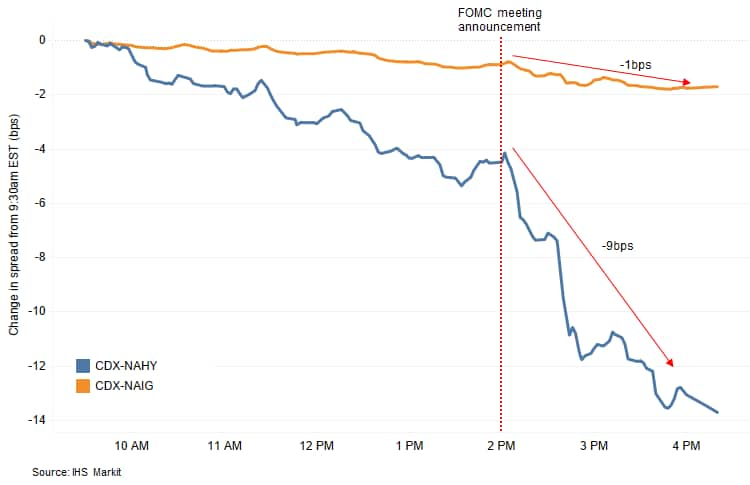
- CDX-NAIG closed -2bps/70bps and CDX-NAHY -18bps/436bps. The
chart below indicates that most of today's tightening in CDX-NAHY
occurred after the FOMC announcement and Fed Chairman Powell's
press conference.
- Crude oil closed +0.6%/$41.27 per barrel.
- In a press release, Hess Corporation reported a second-quarter 2020 net loss of $320 million, compared with a net loss of $6 million in the second quarter of 2019. The adjusted net loss was $320 million, compared with an adjusted net loss of $28 million in the prior-year quarter, primarily due to lower realized selling prices, the company said. Net cash provided by operating activities was $266 million, compared with $675 million a year ago, primarily due to lower realized crude oil selling prices and the impact on cash flows from deferring sales for the 3.7 MMbbl loaded on VLCCs in the quarter, the company said. The Exploration and Production net loss was $249 million in the second-quarter of 2020, compared to a net income of $68 million in the second quarter of 2019. Second quarter E&P adjusted net loss was $249 million, compared with an adjusted net income of $46 million in the second quarter of 2019. Net production, excluding Libya, was 334,000 boe/d, up 22% from 273,000 boe/d in the prior-year quarter, primarily resulted from a 39% increase in Bakken production and production from the Liza Field, offshore Guyana. Bakken net production was 194,000 boe/d (85% liquids), up 39% from 140,000 boe/d in the prior-year quarter, primarily due to increased wells online and improved well performance, the company said. There was no net production for Libya in the quarter due to the declaration of force majeure by the Libyan National Oil Corporation. Hess revised its 2020 production forecast (excluding Libya) at 330,000 boe/d, up from its previous guidance of 320,000 boe/d, announced in May 2020. (IHS Markit Upstream Companies and Transactions' Karan Bhagani)
- Coronavirus cases in the U.S. increased 1.9% as compared with the same time Tuesday to 4.39 million, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University and Bloomberg News. The increase was higher the average 1.6% daily gain over the past week. Deaths rose 1.1% to 149,961. (Bloomberg)
- While coronavirus-induced volatility plagued equity markets in
March, IHS Markit closely monitored daily factor and style model
performance with weekly performance reviews of daily style
exposures. Volatility has since settled down, though still in
excess of levels at the start of the year. Given these unusual
times, with the COVID-19 pandemic wreaking havoc from a health and
financial perspective, we extend our review from both a macro and
factor view during the first six months of this year. (IHS Markit
Research Signals)
- Large caps were favored over small caps through June, while the prolonged growth cycle over value strategies benefited further from a sharp bounce since March
- Price Momentum and Historical Growth factors, such as 24-Month Active Return with 1-Month Lag and 1-yr Change in Sales, respectively, were consistent outperformers, while Deep Value measures suffered, particularly those based on analyst estimates, with Leading 12 Month EBITDA/EV the weakest of the group
- The Historical Growth Model topped all other style models, though the Price Momentum model has been making a comeback since March, while the Deep Value Model sat at the opposite extreme
- The US goods deficit narrowed $4.7 billion in June to $70.6
billion, a larger narrowing than both we and the Bloomberg
consensus estimated. Inventories, though, fell more than expected.
(IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- Both exports +13.9% and imports +4.8% rose considerably more than expected, with the balance implying somewhat more net exports in the second and third quarters.
- The combined inventories of wholesalers and retailers fell sharply in June, as recovering final sales were not met with domestic production.
- In response to these developments, we lowered our estimate of second-quarter GDP growth by 0.2 percentage point to -35.3% and we raised our forecast of third-quarter GDP growth by 0.9 percentage point to +19.8%.
- We expect the pace of recovery to slow in July, however, as households and businesses react with renewed caution to a surge in new COVID-19 infections that began in mid-June and as state and local authorities reimpose some restrictions on activity that had been lifted in May and June.
- The US Pending Home Sales Index (PHSI) jumped 16.6% to 116.1 in
June, its best reading since February 2006. Two months earlier, the
index plunged to an all-time low of 69. (IHS Markit Economist
Patrick Newport)
- For the second month in a row, all four regions posted double-digit gains. The South, which accounted for 46% of existing home sales in June, soared to an all-time high, despite the resurging pandemic (note: the index is an end-of-month measure; daily cases of the pandemic began rising in mid-June).
- Some home price indicators—the median and average price of an existing home, the FHFA seasonally adjusted home price index, and, possibly, the Case-Schiller 10- and 20-city indexes (these are three-month moving averages)—have declined recently. This, along with record low interest rates, is boosting demand.
- Applications to buy homes remains strong, according to the Mortgage Bankers Association. Its Purchase Index for the week ending 24 July was 21% higher than a year earlier, according to a report released today (29 July).
- The PHSI leads existing home sales by a month or two, according to the National Association of Realtors. Expect a solid increase in existing home sales in July or August or both.
- The Alaskan salmon season has improved significantly over the
past four weeks, although many areas of the state remain behind
historical averages. Total salmon harvest to week 30 (July 30,
2020) was 59.4 million fish, with 45% of the catch forecast for
this year realized. "The focus of Alaska's salmon harvest is
shifting from sockeye to pink as Bristol Bay winds down," McDowell
Group economist Garrett Evridge noted in the Alaskan salmon weekly
report produced on behalf of the Alaska Seafood Marketing
Institute. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Estela
Cuesta)
- Nearly 42 million sockeye have been harvested statewide - 40 million in Bristol Bay - a pace 19% behind last year's record production but on par with the 10-year average.
- Around 13.2 million of pink fish have been landed in 2020 to date (week 30), around 5.2% behind the previous year. The current pace is comparable to 2018, but generally behind the longer-term even-year average.
- Four million keta have been landed in 2020, against 11.7 million for the same period in the previous year: "The lowest for this point in the season in at least 12 years, and likely more," Evridge highlighted.
- Coho landings are also trending below typical levels with total harvest of 218,000 fish to date (week 30). "In most years, at least one million coho have been harvested by this point," Evridge said.
- Chinook landings are 29% behind the 2019 pace, reaching 146,000 fish. Harvest in Southeast, however, is ahead of last year.
- IHS Markit has released its latest research on the average age
of vehicles in operation (VIO) in the United States, noting that it
has increased by one month, from 11.8 to 11.9 years, since our
previous study. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Although slight, the increase may generate new business opportunities for companies operating in the aftermarket and vehicle-servicing sector in the US.
- The change partly is a result of lower new vehicle sales in the US, as new vehicle sales provide a pipeline for young vehicles to enter the marketplace.
- IHS Markit's research shows that new vehicles were only 6.1% of the 280,000 million VIO in the US in 2019, compared with 6.7% in 2016.
- On the opposite end is the rate of scrappage pulling vehicles out of the market. In 2019, the scrappage rate as a percentage of vehicles on US roads was 5.1%, compared with 4.6% in 2016, a record sales year for new light vehicles.
- The COVID-19 pandemic is expected to have an impact on the average age of US vehicles in the near term. An older fleet may support replacement sales demand, but retaining cars longer keeps new-vehicle buyers out of the market and delays potential sales.
- Chile's President Sebastián Piñera ratified on 24 July a law
that allows those affiliated with the country's pension fund
administrators to withdraw up to 10% of their accumulated personal
savings. The law took the form of a constitutional reform and was
submitted by opposition parties to help households to access
additional liquidity against the background of financial stress
caused by the COVID-19-virus outbreak. Withdrawals, which are
voluntary and will not be taxed, will be allowed until 24 July
2021. (IHS Markit Country Risk's Carla Selman, Ellie Vorhaben, and
Alejandro Duran-Carrete)
- The measure represents a political defeat for President Sebastián Piñera and is likely to strengthen the opposition ahead of an electoral year. Piñera strongly opposed the initiative, claiming it will further curtail future pension payouts from levels that are already low, but stepped back from challenging it to avoid political damage and the risk of widespread popular protests.
- Opposition left-wing and center-left parties are likely to accelerate and propose deeper changes to planned pension reform under review in Congress.
- The immediate effect will be a boost in spending, limiting initial improvements in banking-sector liquidity. Amounts authorized for withdrawal range from CLP1,000,000 (USD1,300) to CLP4,300,00 (USD5,600). Such withdrawals are likely to be used to boost consumption, especially as the labor market had shed 1.64 million jobs as of May 2020 (with an 18% decrease in employment versus end-December 2019).
- The portfolio of the AFP is likely to be modified to provide enough liquidity for withdrawals. According to the Superintendence of Pensions, roughly CLP32,007 billion of the AFP's assets are allocated into securities issued by financial institutions, mainly bonds of the 10 largest banks by assets.
- There is an increased need for quantitative easing measures to stabilize capital market; the AFP are likely to take more risk.
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- European equity markets closed mixed; France +0.6%, UK flat, Germany/Italy -0.1%, and Spain -0.6%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -2bps, Spain -1bps, and UK/France/Germany +1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/59bps and iTraxx-Xover -4bps/362bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.1%/$44.09 per barrel.
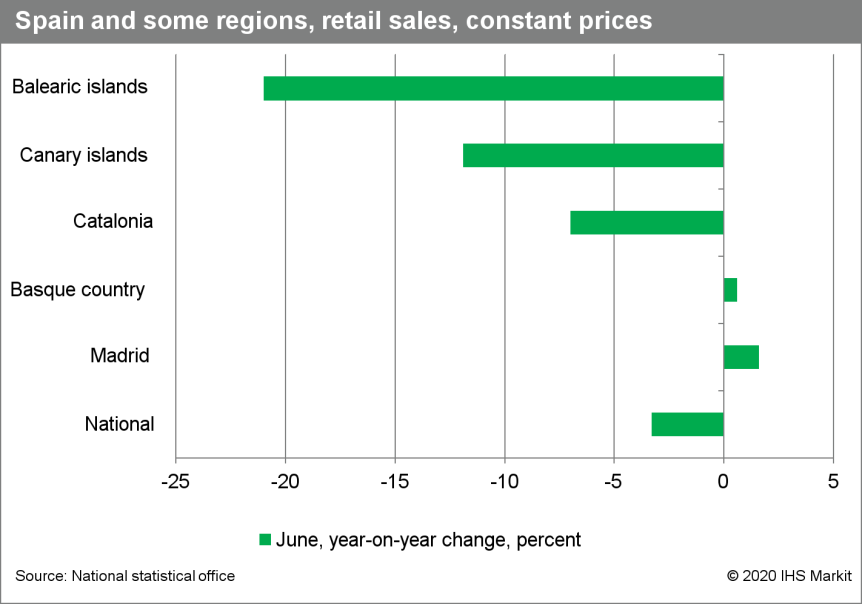
- According to the National Statistics Institute (INE), the
volume of Spain's retail sales rose by 17.8% month-month (m/m) in
June after a 19.4% m/m gain in May. (IHS Markit Economist Raj
Badiani)
- Retail spending still stood 5.4% below its February 2020 level, while remaining 4.7% lower when compared to a year earlier.
- Jittery consumers are likely to spend cautiously in the next few months after the initial relief surge in May and June, fearing the lingering impact of the COVID-19 virus crisis on the economy and the labor market, alongside the risk of infection.
- In addition, foreign visitors are at historic lows, which will
weigh down on the country's retail sector. Indeed, the retail sales
in Spain's tourist hotspots are lagging notably the national
average.
- France's consumer confidence index declined from 96 in June to
94 in July, according to seasonally adjusted figures released by
the National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (Institut
national de la statistique et des études économiques: INSEE). The
index had previously fallen from 105 in February to 92 in May
before rebounding in June. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- The headline index was hit by a sharp fall in households' view of their past standard of living , which worsened to its lowest value since early 2015 (-66, following -57 in June). Moreover, the index measuring households' past financial situation also fell in July, but at a lesser rate (-15 in July versus -12 in June).
- Households' views on their future financial situation and the general economy remained relatively stable following their substantial increase in June. Similarly, the index measuring households' major purchases intentions over the coming year edged downwards following a large rise during the previous month.
- Saving intentions continued to increase in July. Indeed, the related index rose to its highest level since December 2014. Slightly more encouragingly, households' perception of future unemployment eased somewhat from June, but remains elevated by historical standards (76 following 78 in June, well above a long-term average of 33).
- The decline in July's confidence index is partly explained by the lagged impact of the shock experienced since March. However, it also highlights that households are still far from confident about their future financial and general economic outlooks. The increase in the number of cases in some French regions, particularly since mid-July, may have had an influence on the figures.
- Michelin has announced that its financial performance in the
first half of 2020 has slipped to a loss as the COVID-19 virus
pandemic took its toll. For the six months ending 30 June, the
company's sales declined by 20.6% year on year (y/y) to EUR9,357
million. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- At the same time, its segment operating income has dropped by 78.4% y/y to EUR310 million, with its margin tumbling from 12.2% to 3.3%.
- Operating income also contracted from EUR1,341 million to EUR177 million, as net income went from a profit of EUR844 million to a loss of EUR137 million.
- On a segment basis, it revealed that its Automotive & Related Distribution, which focuses on passenger car tires, has fallen by 22.3% y/y to EUR4,394 million, and its operating income dropped from a profit of EUR585 million in the first half of 2019 to a loss of EUR35 million during the most recent period.
- Sales by its Road Transportation & Related Distribution business retreated by 23.3% y/y to EUR2,411 million, as operating income fell to a loss of EUR30 million against a profit of EUR279 million a year ago.
- Revenues at its Specialty Businesses & Related Distribution, which includes construction tires have slipped by 14.3% y/y to EUR2,552 million, while its operating income remained in profit but dropped from EUR574 million to EUR375 million.
- According to the Swedish National Institute of Economic
Research (NIER), Sweden's economic tendency indicator has improved
to 83.4 in July, a marked improvement compared with 64.8 in May and
75.3 in June. However, it remained below the 20-year average of
100, although it has recovered significantly since April's low.
(IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- Manufacturing confidence improved to 95.7, with indicators for capital and consumer goods producers close to historical averages. Retail trade confidence jumped by 11 points in July owing to an improved assessment of stock levels. Confidence in the services sector improved owing to a better demand outlook but remained far below the historical average.
- Contrary to the broad-based improvements, the consumer confidence index declined by almost one point in July to 83.3, down from 84.1 in June. The deterioration is due to a more pessimistic assessment of a good time to make major purchases and the current state of the Swedish economy.
- The latest uptick in confidence indicators suggests a gradual return of activity after the bottom was reached in April. Absent a new shock, we expect this improving trend to continue in the coming months, although the pace is likely to be moderate.
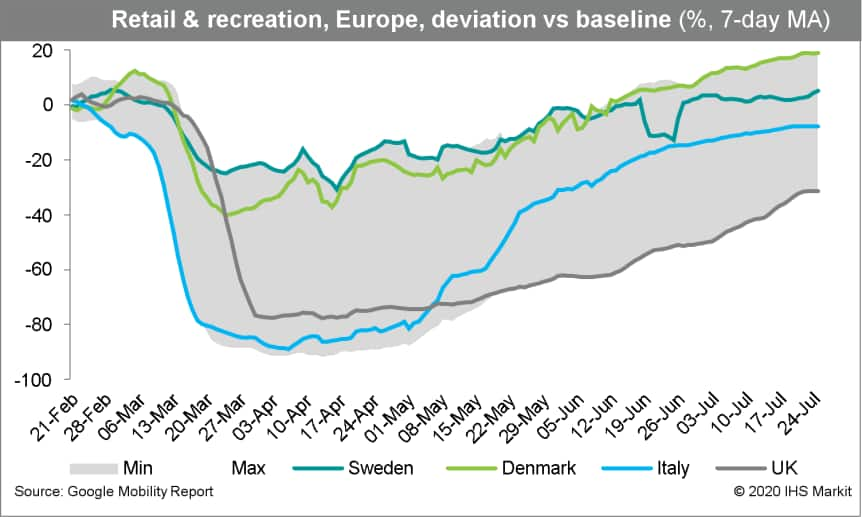
- The mild deterioration among consumers is also visible in other
real-time activity indicators. According to the Google Mobility
Report, footfall in the retail and recreation categories remained
flat in July, compared with the continuous improvements elsewhere
in Europe.
- The National Statistical Institute (NSI) has published the
latest high-frequency data for Bulgaria. Bulgarian industrial
output collapsed in April and May, falling by 16% y/y and 18% y/y,
respectively. The manufacturing sector, specifically transport
equipment and machinery, has been particularly hard hit, reflecting
the impact of the lockdown and social distancing on factories as
well as the collapse of external demand. (IHS Markit Economist
Dragana Ignjatovic)
- Industrial output has fallen by more than 8% y/y in the first five months of 2020.
- The weakness is also evident in the foreign trade data. According to balance of payments statistics released by the Bulgarian National Bank, exports fell by 20% y/y in April and May while imports were down around one-third y/y in both months. This reflects the economic shutdown of Bulgaria's key regional and EU trading partners as well as the collapse of demand from households and industry for imports. In addition, the services balance, which includes tourism receipts, has fallen by three quarters y/y in May alone.
- The effect of the COVID-19 virus was also clearly visible on the retail sector. According to NSI, retail sales collapsed by more than 20% y/y in April and May. The data reflect the implementation of lockdown and social distancing measures by the Bulgarian government in March until mid-May when a moderate easing was initiated.
- In a separate release from NSI, consumer price inflation has undergone a sharp deceleration through most of the second quarter, ticking up modestly in June. Consumer price growth has slowed from an average 3.6% y/y in the first quarter to an average 1.6% y/y in the second, reflecting the global collapse in oil prices (amid oversupply and the drying up of demand) and moderating food price increases.
- Turkish public banks have announced the exclusion of six major automotive manufacturers from their loan packages with low interest rates, reports the Halkbank. The manufacturers are Honda, Hyundai, Fiat, Ford, Renault, and Toyota. The banks' decision was taken because of price rises implemented by the automakers, which could have a negative effect on automotive steel demand in Turkey. Haydar Yenigun, chairperson of the Turkish Automotive Manufacturers' Association and general manager of Ford Otosan, said, "It will definitely have negative effects on our sales, but the amount is not clear yet, we should wait and see." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
- According to the latest customs-based trade results from the
Georgian National Statistical Office (GeoStat), exports from
Georgia in the second quarter contracted by 24.8% year on year
(y/y), after falling by 5.7% y/y in the first quarter. (IHS Markit
Economist Venla Sipilä)
- Contraction of imports intensified to 32.8% y/y, following a downward revised decrease of 3.9% y/y in the first quarter.
- As a result, the trade deficit in April-June narrowed by 38.5% y/y, after easing by a more moderate rate of 2.7% y/y in the first quarter and widening by 3.9% y/y in the final quarter of 2019. The January-June trade gap settled at USD2.0 billion, narrowing by 21.3% y/y, with exports falling by 16% y/y and imports contracting 19% y/y.
- Exports to countries of the European Union (EU) in the second quarter fell around at the average rate, while exports to economies of the Commonwealth of the Independent States (CIS) fell by a particularly high rate of 43% y/y. Georgian EU-imports fell faster than average, and its imports from CIS eased relatively modestly.
- Russia, which in the first half of 2019 had been Georgia's leading export market, with a share of 14.6% of exports, now slid to the third place with a share of 12.5%, with exports collapsing by some 28% y/y. Exports to Turkey, Armenia, Ukraine and Azerbaijan also contracted significantly. Conversely, exports to China soared fourfold, lifting China to the top export destination, from the eighth biggest export market a year earlier.
- Imports from all key supplier countries fell clearly, although relatively modestly (only by 5% y/y) from Russia. Even with a contraction of 18% y/y, Turkey retained its place as the most important import provider, followed by Russia, China and Azerbaijan. Imports from Armenia increased by over a half, lifting its share to 5.6% from 2.9% in January-June 2019.
- Copper ores and concentrates and motor cars remained the top export categories, with shares of around 21% and 12%, respectively. Motor cars, copper ores and concentrates, and petroleum and petroleum products were the leading import goods.
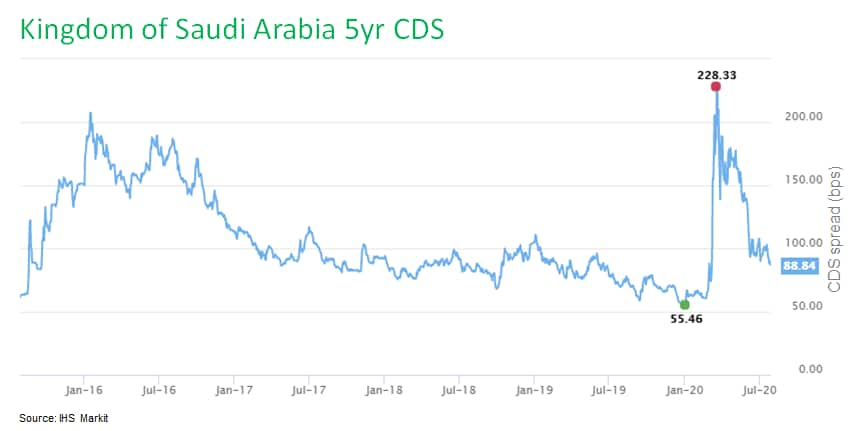
- The Saudi Arabian budget deficit at the end of June reached
more than 75% of the gap expected for the full-year 2020. With the
government trying to control the gap, non-payment risks are rising.
Typically, spending accelerates toward the end of the year, which
is likely to push the government to delay some payments from this
year into next year, and potentially cancel some projects all
together. (IHS Markit Economist Ralf Wiegert)
- Saudi Arabia's government posted a second-quarter deficit equal to SAR109.2 billion (USD29.1 billion) as oil revenues alone fell 45% year on year (y/y), and total revenues dropped by 49% to SAR133.9 billion. The impact of the global pandemic and the low oil price have been responsible for the sharp fall of revenues. Meanwhile spending reached SAR243.2 billion, a 17% y/y decline, with the majority borne by capital expenditures.
- The fiscal deficit for the quarter hit SAR104.7 billion, and the gap for the entire first half of the year equaled SAR143.3 billion, more than three quarters of the SAR186.9-billion deficit penciled in the original budget plan for the full-year 2020.
- Already in June, the government abandoned the cost of living allowance and thus cut spending by SAR45 billion on an annual basis. It has also increased the VAT rate from 5% to 15% as of 1 July. VAT revenues in 2019 were SAR46.7 billion.
- Fiscal results for the second quarter of 2020 have been largely
in accordance with IHS Markit's expectations. For the full-year
2020, we currently project the fiscal deficit to reach SAR346
billion, or 13.8% of GDP, despite the government's efforts to
contain the gap.
- Botswana's GDP growth ticked up to 2.6% year on year (y/y) in
the first quarter, despite the continued poor performance of the
mining sector. IHS Markit expects Botswana's economy to contract by
8.8% in the full year 2020 due to the impact of the COVID-19
pandemic on both the domestic and external economies. (IHS Markit
Economist Archbold Macheka)
- Botswana's economy grew by 2.6% y/y in the first quarter of 2020, up from 1.6% y/y in the previous quarter, latest official data from Statistics Botswana show. The growth was driven largely by the water and electricity; finance and business services; and trade, hotels and restaurants sectors, which saw increases in value added of 13.4%, 6.2%, and 4.4% respectively.
- Support to the growth also came from the transport and communications industry, which saw its value added increase by 2.6% y/y in the first quarter. However, the industry's performance was lowered by a decrease in real value added of the air and rail transport sector due to the suspension of travel caused by COVID-19 virus containment measures.
- Botswana's mining sector continued to struggle in the first quarter, with the real value added of mining contracting for the fourth straight quarter. The 6.1% y/y decline in mining activity in the first quarter was influenced mainly by diamond production, which shrank by 5.7% amid weak global diamond demand. The sector's performance was weighed down by the value added of the ash industry, which was pulled down by an 11.4% y/y fall in soda ash production.
- On the demand side, total final consumption expenditure expanded by 3.5% y/y in the first quarter, with government and household final consumption increasing by 3.9% and 3.4% respectively. Gross fixed capital formation grew by 6.1%, thanks to stronger growth in expenditure on construction and machinery and equipment. Real exports of goods and services contracted 17.3% y/y in the first quarter, pulled down by weak diamond exports (down 39.8%). Real imports of goods and services rose by 8.0% y/y in the first quarter.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; China +2.1%, Hong Kong +0.5%, South Korea +0.3%, Australia -0.2%, India -1.1%, and Japan -1.2%.
- Fitch Ratings has revised its outlook on Japan's long-term
sovereign credit ratings from Stable to Negative, while maintaining
its long- and short-term sovereign credit ratings on the country at
A (20 on the IHS Markit scale) and F1+, respectively. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The revision to Negative reflects Fitch's view that the higher Japanese debt ratio and downside risks to the macroeconomic outlook will exacerbate the challenge of placing the debt ratio on a downward path over the medium term. Fitch projects that Japan's gross general government debt ratio will rise to above 260% of GDP in 2021-21 before turning to a gradual downward path.
- Fitch's current rating is lower than the assessment of IHS Markit (at 5), whereas S&P Global Ratings' sovereign credit rating is at A+ (on the generic scale) and 15 (on the IHS Market scale) with a Stable outlook. Moody's sovereign credit rating is at A1 (on the generic scale) and 15 (on the IHS Markit scale) with a Stable outlook.
- Japan's confirmed COVID-19 cases are still far lower than the country's G7 counterparts, and the fiscal support and expected rebounds in external demand are likely to lead to a gradual recovery in the second half of 2020. Nevertheless, the pandemic has severely affected Japan's economy and Fitch believes a resurgence in cases is creating the possibility of further containment measures and risk to the economic outlook.
- Mitsubishi Motors has announced plans to invest approximately JPY8 billion (USD75.9 million) for the production of a new electric kei car at the Mizushima Plant in Kurashiki city, Okayama Prefecture, beginning in August 2020, according to a company statement. The automaker plans to develop the new electric kei car jointly with Nissan Motor, Mitsubishi's alliance partner. The investment will be directed towards the setting up of assembly and inspection equipment for the drive battery; the expansion of stamping, welding, and painting assembly facilities following a shift to in-house production of drive battery cases; and a line expansion for the manufacturing of electric vehicle (EV) platforms. The investment is in line with the initiatives by the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, unveiled in May, aimed at improving the competitiveness and profitability of all three member companies. Under the model, Nissan will assume leadership in autonomous vehicle operations, while connected car technologies will be led by Renault on Android-based platforms and by Nissan in China. Renault will also lead the core system of the electrical-electronic architecture, E-body, while the e-Powertrain will be led by both Nissan and Renault. Mitsubishi will assume the lead for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) in the C and D segments. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- The South Korean government has launched an investigation into Tesla's Model 3 over possible problems with parts, reports the Yonhap News Agency. The Korea Automobile Testing & Research Institute (KATRI) of the Korea Transportation Safety Authority is looking into whether the Model 3's autopilot driver-assist feature has any safety problems. "The probe will be focused on the anti-lock brake system and the lane-keeping assist system amid reports that the vehicle may have faulty parts related to its autonomous driving program," said an unnamed official at the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MLIT). If the Model 3 turns out to have faulty components, the ministry will order the automaker to recall the model. The investigation will take between six months and one year to complete. Tesla entered the South Korean market in 2017 and currently sells the Model 3, Model S, and Model X there. It has installed around 450 slow-charging stations and 32 superchargers across the country. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Real-Time Innovations (RTI), a software framework provider for smart machines and real-world systems, has joined Baidu's Apollo open-source, full-stack software for autonomous vehicles (AVs). Baidu also developed a domain controller, called Apollo Computing Unit (ACU), integrated with RTI Connext DriveTM software, to enable full stack capability in mass production for car OEMs. Bob Leigh, senior market development director, commercial at RTI, said, "The autonomous vehicle market has experienced rapid growth in the last several years. We developed RTI Connext Drive to give our customers and partners the tools to solve complex autonomy challenges. In joining the Apollo ecosystem, we are looking forward to conquering the challenges hindering autonomous vehicle deployment and adoption as we move into the next phase of autonomy." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-29-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-29-july-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+29+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-29-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 29 July 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-29-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+29+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-29-july-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




