Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jul 30, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 30 July 2020
APAC equity markets closed mixed, while record quarterly declines in German and US Q2 GDP drove all major European and most US markets lower on the day. Government bonds closed higher across Europe and the US, while iTraxx IG/high yield credit indices closed wider and CDX IG/HY was close to flat on the day. The dollar continued its decline, but did little to help gold and oil, which both ended the day lower. US initial claims for unemployment insurance reported the second consecutive week of increases in claims, further illustrating the economic effects of the current second round of mandated business closures aimed at slowing the spread of COVID-19.
Americas
- Most US markets closed lower, except for the Nasdaq +0.4%, with all closing near the highest levels of the day after a weak open; DJIA -0.9% and Russell 2000/S&P 500 -0.4%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -2bps/0.56% yield and 30yr bonds closed -3bps/1.21% yield. 5yr US govt bonds closed at a new all-time low yield of 0.22%.
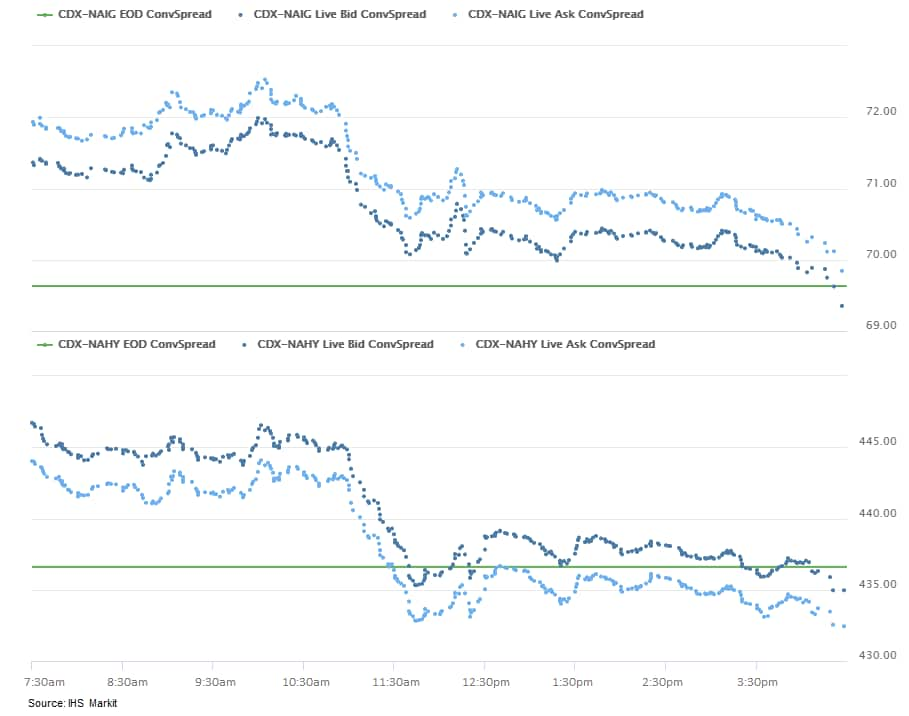
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/70bps and CDX-NAHY -4bps/434bps. CDX-NAIG
was as wide as +2bps and CDX-NAHY +8bps shortly after the US equity
market open, but switched course and began tightening after 10:30am
EST.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.5%/92.94 and is now at the lowest level since early-May 2018.
- Gold closed -0.6%/$1,942 per ounce, but was down as much as -1.2% at 11:10am EST.
- Crude oil closed -3.3%/$39.92 per barrel.
- Amazon reported record revenue and profit even as it spent $4 billion between April and June to stabilize its supply chain and improve worker safety. The Seattle e-commerce pioneer now employs more than 1 million workers, the second-largest in the U.S. Amazon reported $88.9 billion in sales as a flood of customers grew to rely more than ever on online shopping. Profits doubled to a record $5.2 billion, far exceeding analyst expectations. (WSJ)
- US GDP fell at a 32.9% annual rate in the second quarter,
according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis's (BEA's) "advance
estimate," as businesses and households curtailed activities in
response to COVID-19 and "stay-at-home" orders. Some activities
resumed over May and June as those orders were relaxed. Businesses
and households were recipients of substantial federal fiscal
stimulus. (IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny, Michael Konidaris,
and Lawrence Nelson)
- Within GDP, final sales to domestic purchases fell at a 28.2% annual rate in the second quarter, as all of its major components fell sharply, including personal consumption expenditures (down 34.6%), business fixed investment (down 27.0%), and residential investment (down 38.7%).
- Outside of final sales to domestic purchasers, inventory investment fell $235 billion to a deeply negative level (-$316 billion).
- The only major components of GDP to post increases in the second quarter were government consumption and gross investment (up 2.7%) and net exports (up $7 billion). Declines in both final sales (down 29.3%) and final sales to domestic purchasers (down 28.2%) were slightly less severe than we had anticipated.
- Federal stimulus had major effects on incomes. Disposable personal income surged 42.1% in the second quarter, as transfer payments rose more than $2.4 trillion. This more than offset a $795 billion decline in labor compensation as employment and wages tumbled.
- Inflation was deeply negative in the second quarter and close to our expectations. The GDP price index fell at a 1.8% rate, down from a 1.4% increase in the first quarter.
- The core personal consumption expenditure (PCE) index fell at a 1.1% rate in the second quarter, down from a 1.6% increase in the first quarter.
- Seasonally adjusted US initial claims for unemployment
insurance, at 1,434,000 in the week ended 25 July, remained at
historically high levels, although well below the all-time high of
6,867,000 in the week ended 28 March. Since the initial spike in
mid-March, initial claims have remained at levels unprecedented
before the COVID-19 pandemic, averaging 1.434 million per week over
the last eight weeks.
- The seasonally adjusted number of continuing claims (in regular state programs), which lags initial claims by a week, rose by 867,000 to 17,018,000 in the week ended 18 July; this was the first increase in continuing claims in nine weeks.
- The insured unemployment rate in the week ended 18 July rose 0.5 percentage point to 11.6%.
- There were 829,697 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 25 July. In the week ended 11 July, continuing claims for PUA fell by 766,558 to 12,413,322.
- In the week ended 11 July, 1,055,098 individuals were receiving Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) benefits.
- The Department of Labor provides the total number of people claiming benefits under all its programs with a two-week lag. In the week ended 11 July, the unadjusted total fell by 1,601,699 to 30,202,498. Of this total, 54% are from regular state programs and 41% from the PUA program.
- Navitas Petroleum says Blackstone, through Beacon Offshore Energy, is buying LLOG's 31% interest in the Shenandoah project, while Navitas will continue to hold 53% stake. Navitas Petroleum says Blackstone Group signed a preliminary deal to raise its stake to 47% from 16% in the project and will operate the Shenandoah project. The Shenandoah development plan consists of four production wells and a new floating production semi that will have a production capacity of over 70,000 BOE/d and sit in a 1,750 m (5,740 ft) water depth. TechnipFMC was selected to supply the subsea trees, which are to be designed for pressures up to 20,000 pounds per square inch (PSI). Reports also indicate that Exmar will supply its OPTI design for the semisubmersible hull. Navitas said the Shenandoah project is expected to generate USD 1.13 billion in cash flow for the company. First oil is expected in 2024. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Kelvin Sam)
- In a press release, ConocoPhillips reported second-quarter 2020
earnings of $0.3 billion, compared with second-quarter 2019
earnings of $1.6 billion. The decrease in earnings reflected lower
realized prices and lower volumes, partially offset by a change in
Cenovus Energy equity market value and a gain from the
Australia-West divestiture, the company said. (IHS Markit Upstream
Companies and Transactions' Karan Bhagani)
- Adjusted loss was $994 million, down from adjusted earnings of $1,143 million a year ago. The decrease in adjusted earnings reflected lower realized prices and volumes, partially offset by lower depreciation expense and production and operating expenses associated with the lower volumes, the company said.
- Special items for the current quarter were primarily due to a realized gain on the completion of the Australia-West divestiture and an unrealized gain on Cenovus Energy equity, the company said.
- The company's total realized price was $23.09/boe, down 54% from $50.50/boe a year ago, reflecting lower marker prices regional differentials.
- Production excluding Libya was 981,000 boe/d, down 309,000 boe/d, or 26%, from a year ago.
- After adjusting for the closed dispositions, production decreased by 212,000 boe/d. The decrease in production was primarily due to curtailments and normal field decline, partially offset by growth from the Big 3 and development programs in Canada and Europe, the company said. There was no production from Libya as it remained in force majeure during the quarter.
- In the second quarter, General Motor's vehicle production was
halted for eight weeks in North and South America because of
efforts to contain the spread of the COVID-19 virus, creating the
most challenging quarter that GM (or the industry) has faced in
decades. Amid those conditions, GM's sales and production declined,
and the automaker has reported losses during the second quarter,
although over the first half the group remained profitable. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- GM has reported a net loss (attributable to common stockholders) of USD806 million in the second quarter.
- GM's wholesale deliveries dropped 62.7% year on year (y/y) to 421,000 units in the second quarter; the wholesale deliveries do not include those of joint ventures (JVs).
- GM also saw a 24.3% y/y decline in retail deliveries in the second quarter, which does include JVs.
- In China, in the second quarter, economic activity began to open up and GM's retail sales in Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa declined 6.1% y/y in the second quarter.
- In the second quarter, GM's North American retail sales dropped 35.5% y/y. In volume terms, GM's wholesales declined 708,000 units and retail sales dropped 472,000 units globally.
- Despite a difficult second quarter for the automotive industry and the global economy as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, GM's efforts in recent years to ensure a strong foundation, as well as its austerity measures, helped the company to withstand the effects of the pandemic.
- During the second-quarter earnings call, GM confirmed that construction has started on its Ultium Cells LLC battery plant in the United States and confirmed that the Hummer by GMC EV is to be revealed in the fall in the US, likely during the fourth quarter.
- Fairfax county in the US state of Virginia has started test runs of an autonomous electric shuttle, called Relay. The shuttle will carry passengers and provide first- and last-mile connections between the Dunn Loring Metrorail Station and Mosaic district in Fairfax county. This pilot project will use EasyMile's EZ10, a fully electric shuttle bus that is capable of Level 4 autonomous operation and is deployed with LiDARs, cameras, and GPS to ensure safety. The shuttle will be operated by Transdev, which will maintain and manage the vehicle. This pilot project is a partnership between Fairfax county, Dominion Energy, EDENS (Mosaic), the Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT), the Virginia Tech Transportation Institute (VTTI), and George Mason University (GMU). (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- DuPont reports a second-quarter net loss of $2.5 billion,
reflecting the impact of a $2.5-billion noncash impairment charge
in the transportation and industrial segment and restructuring
costs. Adjusted earnings were $514 million, down 19% year on year
(YOY). Reported adjusted earnings of 70 cts/share were down 30% YOY
and 11 cts/share above consensus estimates, as reported by Zacks
Investment Research. Net sales of $4.8 billion were down 12% YOY.
Organic sales and volumes were both down 10% YOY.
- The electronics and imaging segment reported second-quarter net sales of $905 million, up 5% YOY. Operating EBITDA for the segment was $277 million, up 13% YOY driven primarily by volume gains in semiconductor technologies and cost productivity actions. Strong volume gains in semiconductor technologies more than offset weaker demand in interconnect solutions and image solutions.
- The nutrition and biosciences segment reported net sales of $1.5 billion, down 1% YOY. Operating EBITDA for the segment was $418 million, an increase of 8% YOY. Favorable product mix led by gains in probiotics and animal nutrition, as well as cost productivity actions, generated the improvement in operating EBITDA margins.
- Transportation and industrial reported net sales of $832 million, down 34% YOY. Operating EBITDA for the segment was $49 million, a decrease of 86% YOY, driven primarily by charges of approximately $130 million associated with temporarily idling approximately 50% of polymer capacity to align supply with demand. Volume declined 28% due to lower auto builds, as global automotive production was down approximately 45% YOY. The impact of COVID-19 on other key industrial markets, in addition to automotive, contributed to the double-digit volume declines.
- Safety and construction reported net sales of $1.2 billion, down 7% YOY. Operating EBITDA totaled $349 million, a decrease of 9% YOY, primarily from lower volumes partially offset by cost productivity actions and favorable product mix.
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- European equity markets closed sharply lower; Germany -3.5%, Italy -3.3%, Spain -2.9%, UK -2.3%, and France -2.1%.
- 10yr Europe govt bonds closed higher across the region; Germany/France -4bps and UK/Italy/Spain -3bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +2bps/61bps and iTraxx-Xover +15bps/377bps.
- Brent crude closed -1.9%/$43.25 per barrel.
- Germany's GDP plunged by 10.1% quarter on quarter (q/q) and
11.7% year on year (y/y) in the second quarter, both record
declines by some distance. In comparison, the largest q/q decline
during the global financial crisis was 4.7% in the first quarter of
2009 and the largest y/y drop was 7.9% in the second quarter of
2009. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- The second-quarter q/q decline was larger than market consensus expectations (-9.0%, according to Refinitiv's survey) and our own more pessimistic estimate (-9.5%). A slight upward revision to the first quarter's initially reported decline (from -2.2% to -2.0%) provides a partial offset.
- A complete expenditure breakdown for the second quarter will only follow on 25 August, but the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis) confirmed that, as in the first quarter, extreme weaknesses were broad-based across expenditure components owing to the most intensive phase of COVID-19 virus-related restrictions early in the quarter. Public consumption was the only exception.
- The second quarter experienced "massive" slumps in exports and imports of goods and services, households' final consumption expenditure, and machinery and equipment investment.
- The BMW Group is working to make its next-generation battery cells as recyclable as possible, according to a company statement. The company's new battery cell competence centre will look at the entire sourcing and production cycle for the battery cells, from the selection of materials, to battery cell composition and design, to near-standard production and recycling. Commenting, BMW board member Milan Nedeljkovićsaid, "The new pilot plant will strengthen our expertise in production of battery cells. We will be capable of testing new systems technology and innovative production processes. Our goal is to optimise near-standard production of battery cells from the perspective of quality, performance and costs. The new pilot plant will enable us to close the final gap in the value chain from battery cell development, to production of modules and powertrain components, all the way to installation of fully assembled high-voltage batteries at our vehicle plants. This makes us the first car manufacturer to cover the entire process chain for electric driving." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- Northvolt has announced that it has raised USD1.6 billion in debt financing to support the expansion of its business. The company said in a statement that the latest funds have come via a consortium of commercial banks and pension funds including APG, BNP Paribas, Danske Bank, Danica Pension, IMI-Intesa Sanpaolo, ING, KfW IPEX-Bank, PFA Pension, SEB, Siemens Bank, SMBC, Société Générale, Swedbank, and UniCredit. This is alongside a number of public financial institutions such as the European Investment Bank, the Nordic Investment Bank, and the Export-Import Bank of Korea (KEXIM). The company also noted that the loan is structured with certain guarantees from Nippon Export and Investment Insurance (NEXI), BPI France, and insurance company Euler Hermes, with the latter subject to final approval. Northvolt chief financial officer (CFO) Alexander Hartman said, "The fact that we have these world-class financial institutions supporting a new industry in Europe is a clear sign of where the markets are headed and the opportunity that brings for sustainable projects. This new industrial landscape will need significant investments over the coming years." This latest funding brings the total amount of debt and equity raised by Northvolt to USD3 billion. This is to support the development of its two gigafactories for lithium-ion battery cell production: Northvolt Ett in Skellefteå (Sweden), construction of which will begin in 2021 and which has the potential to manufacture 40 GWh per annum; and Northvolt Zwei in Salzgitter (Germany), which is being developed jointly with Volkswagen (VW) Group and is scheduled to begin production in 2024 with a potential output of 20 GWh. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- According to the 'flash' GDP estimate published by the Austrian
Institute of Economic Research (WIFO), Austrian economic output
collapsed by 10.7% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the second
quarter, following a drop of 2.3% q/q during the first quarter.
(IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- In year-on-year (y/y) terms, Austria's GDP fell by 12.8%. Both the y/y and q/q contractions in activity were the largest since the Second World War.
- The COVID-19 virus-led decline in activity was felt in all expenditure components, with the exception of public consumption, which rose by 1.0% q/q, as the government bolstered public activities in the healthcare sector amid other extra spending to limit the impact of the pandemic.
- The closure of much of the retail and services sectors for most of the quarter led to a substantial decline in private consumption. It collapsed by 12.0% q/q, following a decline of 3.3% q/q during the first quarter.
- Fixed investment declined at a more moderate, but still strong, 7.5% q/q during the second quarter. As usual, the WIFO does not quantify the relative contributions of investment in equipment and construction specifically. However, the relatively modest decline in construction in value-added terms (-3.5% q/q) suggests that the decline in investment in equipment and machinery was particularly strong during the second quarter.
- The economic sentiment indicator (ESI) for the eurozone rose in
July for the third successive month. Despite the sizeable
6-percentage-point rise, the ESI has yet to claw back even half of
its losses between February and April. At 82.3 in July, the index
remains over 17 percentage points below its average since 1999.
(IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Three of the five key sectors showed marked improvements in July - industry, services, and retail - although across-the-board sentiment indices remained well below their pre-COVID 19-virus levels.
- The standout underperformer remains services sentiment. Despite a very strong 9-percentage-point rise in July, the index remained 34 percentage points below its average since 1999.
- In line with the earlier 'flash' estimate, consumer sentiment also slipped back in July, albeit modestly, only four percentage points below its long-run average. The breakdown by sub-component highlighted receding concerns over high unemployment in the past couple of months, but the likelihood of further increases is likely to weigh down on both sentiment and spending beyond the initial bounce owing to the easing of the COVID-19-virus restrictions.
- The rate of unemployment in the eurozone rose only modestly in June, from 7.7% to 7.8%, but given upward revisions to prior months' data, the rate ended up more than half a percentage point above its February and March cycle low of 7.2%.
- Unemployment rose by over 800,000 in the three months to June, the largest increase since May 2009 but around half the scale of the peak increases at the height of the global financial crisis. Still, as previously highlighted, distortions to participation rates due to the COVID-19-virus disruption, along with the government's furlough schemes, are temporarily dampening the unemployment rate.
- Lags between economic weaknesses and headcount adjustment are also an issue. Surveys of employment intentions in the ESI release continue to signal large-scale job losses across sectors, although there has been some recovery in recent months.
- Looking at the largest eurozone member states, July's ESI data showed a continuation of the improvement since May, although the levels remain well below where they were before the COVID-19 virus shock, particularly in Italy.
- Arkema today reported a decline in second-quarter sales and
earnings as the global economy battles against the COVID-19
pandemic.
- EBITDA was down 29.7% year on year (YOY) at €286 million ($336.2 million) with both segments recording a drop.
- Specialty materials EBITDA was 23.4% lower at €233 million, while intermediates saw a 48.0% decline to €66 million.
- EBITDA margin was down from 18.1% in the second quarter of 2019 to 15.0% in the latest quarter.
- Adjusted net income at €90 million was 53.1% lower YOY. Sales declined 15.6% to €1.9 billion on significant slowdown in the construction, transportation, and industrial sectors, overshadowing good demand in the nutrition, packaging, and hygiene markets.
- Sales volumes were down 12.2%, impacted by the lockdown measures imposed in many countries during the quarter.
- Arkema continues to streamline its portfolio with the aim to become a leading specialty materials company by 2024. The company has divested its functional polyolefins business and is in the process of acquiring Fixatti, reinforcing its adhesives operations.
- The company's organic growth ambitions have been supported by a partnership with Nutrien covering the supply of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride, and progress made in the construction of a biobased polymer plant in Singapore.
- In its outlook for the whole of 2020, Arkema says it expects demand will continue to gradually improve in the second part of the year, while remaining below last year's level.
- In a press release, Total reported second quarter 2020 adjusted
net income of $126 million, down 96% from $2,887 million a year
ago. The decrease was primarily due to lower Brent prices, natural
gas prices and refining margins as well as the impact of Covid-19
crisis on demand, the company said. (IHS Markit Upstream Companies
and Transactions' Karan Bhagani)
- Net loss was $8,369 million, down from $2,756 million of net income a year ago, primarily due to asset impairments of $8.1 billion (including $7 billion of Canadian oilsands assets), the company said.
- Operating cash flow before changes in working capital was $3,148 million, down 53% from a year ago.
- Exploration & Production segment adjusted loss was $209 million, down from an adjusted income of $2,022 million a year ago. The decrease was primarily due to the sharp decline in oil and gas prices and lower production.
- Total hydrocarbon production was 2,846,000 boe/d, down 4% from a year ago. The decrease was primarily due to compliance with OPEC+ quotas, mainly in the United Arab Emirates, Nigeria, Angola and Kazakhstan, voluntary reduction in Canada, disruptions in Libya, lower gas demand due to pandemic and natural decline of fields. The decrease was offset by start-up and ramp-up of new projects, mainly Culzean (UK), Johan Sverdrup (Norway), Iara (Brazil) and Tempa Rossa (Italy), the company said. Liquids production was 1,553,000 b/d and gas production was 7,045 Mcf/d, both down4% from a year ago.
- Refining & Chemicals segment adjusted income was $575 million, down 20% from a year ago. The decrease was primarily due to degraded refining margin environment in the quarter and low plant utilization of 59%, partially offset by resilient petrochemical margins and outperformance of trading activities.
- Refinery throughput was down 22% due to extended planned shutdown at Feyzin in France, the decision to not restart Grandpuits after a major turnaround due to the drop in demand and the shutdown of distillation unit at the Normandy platform following an incident at the end of 2019, the company said.
- Gas, Renewables & Power adjusted income was $326 million, down 24% from a year ago.
- Considering the implementation of OPEC+ quotas and the situation in Libya, Total expects its 2020 production to be between 2.9 - 2.95 MMboe/d.
- In April 2020, Total signed an agreement to acquire Tullow Oil's entire stake in the Lake Albert assets for a total consideration of $575 million in cash plus contingent payments.
- On 30 July 2020, Total announced the signing an agreement to sell its interest in seven non-operated mature fields and operated interest in the Cap Lopez oil terminal to Perenco for a total consideration of $290 - 350 million, depending on future Brent prices.
- Offshore drilling contractor Transocean Ltd. reported a net
loss of USD497 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020.
(IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Matthew Donovan)
- This compares to a net loss of USD208 million in the second quarter of 2019 and a first quarter 2020 net loss of USD392 million.
- The second quarter 2020 results included net unfavorable items of USD496 million' Transocean mentioned a USD430 million loss on impairment of assets, a USD59 million loss on impairment of an investment in an unconsolidated affiliate, USD10 million related to discrete tax items and USD1 million in restructuring costs. These were partially offset by a USD 4 million gain on retirement of debt.
- After consideration of these net unfavorable items, second quarter 2020 adjusted net loss was USD1 million.
- Total contract drilling revenues were USD930 million in the second quarter of 2020 compared with USD759 million in the first quarter of 2020.
- The sequential increase was primarily attributed to USD177 million of revenues recognized in second quarter 2020, resulting from a settlement agreement with a customer for performance disputes.
- Additionally, the company received an early termination fee of USD21 million for the semisubmersible Paul B. Loyd Jr., which had its drilling contract terminated.
- This was offset by reductions in day rates and a non-cash revenue reduction from contract intangible amortization associated with Transocean's acquisitions of Songa Offshore and Ocean Rig.
- After widening sharply over the prior 10 months, Turkey's
merchandise trade deficit narrowed in June compared with a year
earlier. However, a fresh, sharp drop in the lira vis-à-vis the
euro, which has also pulled the lira down against the US dollar,
has overshadowed that news. With reserves depleted, the lira is in
danger of suffering further, substantial losses that reflect a
brewing external-financing crisis. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew
Birch)
- Turkey posted a merchandise trade deficit of USD2.846 billion in June, according to customs-based data provided by the Turkish Statistical Institute (TurkStat). For the first time since September 2019, the trade gap was smaller than it had been a year earlier. In the 10 months from October 2019-May 2020, Turkey's trade deficit surged by more than USD17 billion - equivalent to nearly 3% of projected 2020 GDP - compared with a year earlier.
- The spread of the COVID-19 virus to the European Union exacerbated already fading demand from Turkey's biggest export partner. While export losses continued to many EU partners in June, there was a 12.3% year-on-year (y/y) uptick in shipments to Germany, providing a lift to overall EU exports.
- The weaker lira vis-à-vis the euro has improved Turkish export competitiveness, particularly as the European production cycle slowly begins to accelerate after the COVID-19 virus-related shutdown. While the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (Türkiye Cumhuriyet Merkez Bankası: TCMB) had stabilized the lira against the US dollar from mid-May to very recently, the Turkish currency has been depreciating against the euro since early July.
- The depreciation against the euro has been particularly sharp since 21 March as concerns regarding potential European sanctions against Turkey have emerged in response to Turkey's drilling plans in the eastern Mediterranean.
- The Turkish lira continues to come under significant pressure, breaching ₺7.00/USD intraday today for the first time since mid-May:
- Toyota South Africa Motors (TSAM) has confirmed that it is to make an investment of ZAR2.5 billion (USD151 million) in South Africa to establish a new production line as part of the first 'hybrid synergy drive' car project in Durban, reports All Africa News. KwaZulu-Natal (KZN) provincial Member of the Executive Council (MEC) for Economic Development Nomusa Dube-Ncube said that she was "encouraged by the strong commitment displayed by TSAM chief executive Andrew Kirby and Nigel Ward, the group's manufacturing executive vice-president". Dube-Ncube thanked the automaker for its "willingness to work with the KZN government to turn around the situation despite challenges created by the outbreak of Covid-19". According to the news source, Toyota had successful negotiations with the KZN economic development authorities in February on setting up a base in South Africa's automotive supplier park. The country's economic development authorities have also projected the creation of 1,339 jobs with an investment of ZAR2.2 billion. South Africa is in the process of development of an automotive supplier park special economic zone, located in Durban and expected to be operational in 2021. The country wants to promote the use of electric vehicles (EVs) by additional investment in research-and-development infrastructure. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Australia +0.7%, South Korea +0.2%, India -0.9%, Hong Kong -0.7%, Japan -0.3%, and China -0.2%.
- The slip into deflation arose from the Australian government's
free childcare program, a collapse in oil prices, and falling
housing rents. The unwinding of the childcare benefit will boost
current quarter inflation, but otherwise subdued demand should
contain inflation, keeping it below the Reserve Bank of Australia's
2-3% target range well into 2021. (IHS Markit Economist Bree Neff)
- According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) chief economist, Australia has only recorded negative year-on-year (y/y) inflation three times since its series started in 1949, with the last time being during the Asia Crisis.
- Historical data pre-1949 from the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) indicate that the 1.9% quarter-on-quarter (q/q) plunge in inflation during the June-quarter (second quarter) was the largest since the Great Depression.
- The greatest contributor to the plunge in the June-quarter's inflation was childcare, which plunged 95% q/q in response to the one-off benefit offered as part of the government's stimulus package, and lasted from 6 April to 28 June.
- Housing rent costs also fell in quarterly terms for the first time since 1972 (down 1.3% q/q) because of increasing vacancy rates from lockdown measures and rising unemployment.
- A 19% q/q plunge in petrol prices further helped encourage the dip into deflation.
- On the other hand, stockpiling and increased working from home during the June-quarter drove up prices of food, non-durable household equipment (including toilet paper and cleaning products), and durable household equipment such as home office furniture and refrigerators and freezers.
- The June-quarter's plunge in inflation was more significant than IHS Markit had anticipated; as a result, we will be downgrading our 2020 annual average inflation forecast from 1.0%, perhaps closer to the 0.5% range. We assess that deflation may not persist beyond the current quarter especially as the free childcare benefit is unwound and petrol prices are expected to continue gradually drifting upward.
- As childcare costs are included in the two core inflation measures - trimmed mean and weighted median - they made a significant contribution to the weaker core inflation readings during the quarter.
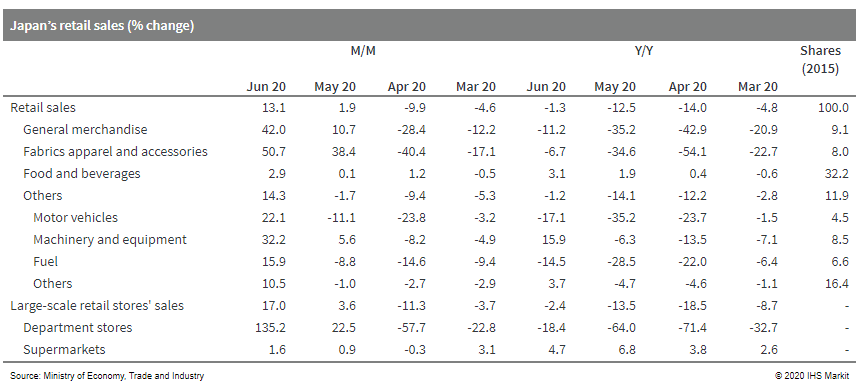
- Japan's retail sales rose by 13.1% month on month (m/m), and
the year-on-year (y/y) contraction narrowed to -1.3% in June in
line with easing containment measures in late May. The
better-than-expected improvement largely reflected the reopening of
non-essential stores, which boosted sales of general merchandise
(including department stores), fabrics apparel and accessories, and
motor vehicles. (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Changes in stay-home/working-from-home lifestyles also continued to support sales of machinery and equipment such as audio and visual appliances, information appliances, home electric appliances, interior products, and gardening and exterior products. Sales of food and healthcare goods remained solid.
- Despite the solid rebound in June, retail sales declined by
7.5% from the previous quarter in the first quarter of 2020, the
largest quarter-on-quarter drop since the second quarter of 1997
(after the first consumption tax increase). Given that containment
measures severely affected consumer-related services, sluggish
retail sales in the first quarter of 2020 point to a significant
decline in private consumption leading to the third straight
quarter of contraction of real GDP in the second quarter.
- Toyota Group has reported a 24.3% year-on-year (y/y) decrease
in overall global output to 673,424 units during June. This figure
includes output at its subsidiaries Daihatsu Motor and Hino Motors.
(IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin Budhiraja)
- According to the data released by the automaker, worldwide output of the Toyota brand was down by 24.0% y/y to 588,816 units last month, Daihatsu's output fell 23.6% y/y to 76,382 units, and Hino's production declined by 44.2% y/y to 8,226 units.
- By region, Toyota Group's production fell by 37.0% y/y in the domestic market to 236,531 units and by 15.0% y/y in overseas markets to 436,893 units. Japanese output of the Toyota brand was down by 44.8% y/y to 159,907 units.
- Production volumes for Daihatsu were down by 5.5% y/y to 69,434 units during June, while those for Hino fell 41.8% y/y to 7,190 units.
- In overseas markets, production of the Toyota brand during June was down by 11.6% y/y to 428,909 units, while Daihatsu posted a 73.7% y/y decline to 6,948 units and Hino's output declined by 56.3% y/y to 1,036 units.
- In the year to date, Toyota Group's global production has declined by 28.1% y/y to 3.926 million units.
- The Toyota brand's output is down by 28.6% y/y at 3.313 million units, while production at Daihatsu is down by 24.1% y/y at 546,064 units and Hino's output is down 36.0% y/y at 67,083 units.
- Under the economic recession and monetary easing during the
pandemic, the leverage ratio of China's macro economy rose by 21
percentage points in the first half to 266.4% at the end of June,
according to a quarterly report by the National Institution of
Finance and Development (NIFD), a government think tank established
by the China Academy of Social Sciences. (IHS Markit Economist
Yating Xu)
- By sector, leverage ratio of corporate sector rose by 13.1 percentage points in the first half, contributing to 60% of the headline increase. Leverage ratio in government and household sector rose by 4.0 and 3.9 percentage points respectively.
- The leverage ratio increased by 7.1 percentage points in the second quarter, significantly slowing from a 13.9-point rise in the first quarter, which was the second largest increase since the first quarter of 2009. However, the growth of total debt, M2 and, total social financing (TSF) in the second quarter all accelerated from the first quarter.
- The softer rise of leverage ratio in the second quarter was entirely because of the economic recovery, while the expansion of debt level accelerated. M2 and TSF grew 12.4% and 11.1% year on year respectively by the end of June, compared with 11.1% and 10.1% at the end of March.
- Preliminary data show that Hong Kong SAR's real GDP slumped 9%
year on year (y/y) in the second quarter, marking the fourth
straight quarter of y/y contraction and after plunging 9.1% y/y in
the first quarter. The above-9% y/y economic slump in the first
half of the year came in the largest on record. (IHS Markit
Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
- In seasonally adjusted terms, the economy showed signs of stabilizing with a mere 0.1% fall from the previous quarter, narrowing sharply from a 5.5% drop in the first quarter. It also represented the smallest quarter-on-quarter decline since the first quarter of last year.
- Private consumption slumped at a faster pace in the second quarter as consumer sentiment remained dampened by the pandemic and local consumption and tourism activities remained at a standstill, despite a gradual easing in social distancing measures. Private consumption dropped 14.5% y/y in the second quarter, accelerating from a 10.6% y/y contraction in the first quarter. It also marked the largest decline in history.
- This reflected a continued slump in retail sales during April and May, down 33-36% y/y, as visitor arrivals plunged 99.9% y/y for both months, driven by a 99.9% y/y slump in tourists from mainland China. Nonetheless, the rate of contractions in retail sales moderated from the 42-44% y/y plunge in February-March as the outbreak in the territory came mostly under control during the second quarter.
- Consumer sentiment was also battered by a deteriorating labor market as the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate skyrocketed to a fresh 15-year high of 6.2% in June, worsening from 5.9% in May. The increase in the jobless rate occurred across the major economic sectors, driven by the sectors hit hard by the pandemic.
- The unemployment rate of the consumption- and tourism-related sectors surged to 10.7%, marking the highest reading since the outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003. Among them, the jobless rate in the food and beverage service sectors jumped to 14.7%.
- Hyundai Motor Group has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with three South Korean car rental companies, LOTTE Rental, SK Rent-a-Car, and Soka to create a new mobility ecosystem. Under this partnership, Hyundai will deploy a data exchange system in vehicles that will help in upgrading services and creating new businesses. Data exchange will be conducted through Developers, an open data platform operated by Hyundai Motor Group. Kyung-lim Yoon, vice president of the open innovation strategy division at Hyundai Motor Group, said, "Hyundai Motor Group will use the strengths of vehicle manufacturers to supply data platforms along with vehicles to major mobility providers. We will actively cooperate to provide the service that we have." Hyundai has signed several agreements with taxi operators and car-sharing service providers in Australia, Germany, India, the Netherlands, Singapore, and South Korea. These partnerships are valuable for Hyundai as they offer an opportunity to enhance the visibility of its vehicles. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer Li Auto is set to raise USD1.1 billion in its initial public offering (IPO) in the United States after selling shares to investors for more than it expected, reports Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter. Li Auto priced 95 million shares at USD11.50 per share, above its initial price target of between USD8 and USD10 per share. The news, which emerged one day before Li Auto's official listing on the Nasdaq Stock Market, indicates that the startup's US IPO seems to be going as planned. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-30-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-30-july-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+30+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-30-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 30 July 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-30-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+30+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-30-july-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




