Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jul 21, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 21 July 2020
Most global equity markets closed higher today, except for US technology stocks, with the positive momentum that began during the APAC trading session rapidly dropping off during the last hour of trading in the US. US and European credit indices closed relatively flat, while commodities closed higher on weakness in the US dollar.
Americas
- Most US equity markets closed higher, except for the Nasdaq -0.8%; Russell 2000 +1.3%, DJIA +0.6%, and S&P 500 +0.2%. Sentiment shifted to a more negative tone across US equities and credit beginning around 3:00pm EST.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -1bp/0.60% yield, which is the best close since late-April. 5yr bonds reached an all-time low yield of 0.25% today before closing at -1bp/0.27% yield.
- The DXY US Dollar index -0.7%/95.17 is currently at its lowest point since 9 March.
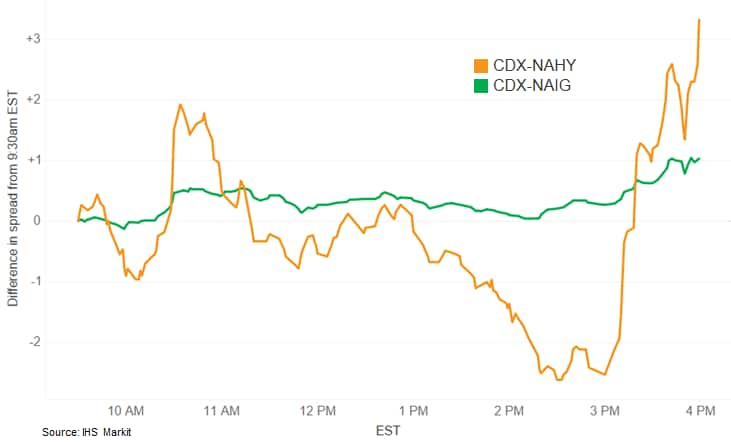
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/70bps and CDX-NAHY -5bps/458bps. The below
chart shows today's intraday changes in CDX spreads beginning at
the start of the US equity trading session:
- Crude oil closed +2.4%/$41.92 per barrel, which is its best close since 5 March.
- Silver closed at +6.8%/$21.56 per ounce, which is its highest close since October 2013.
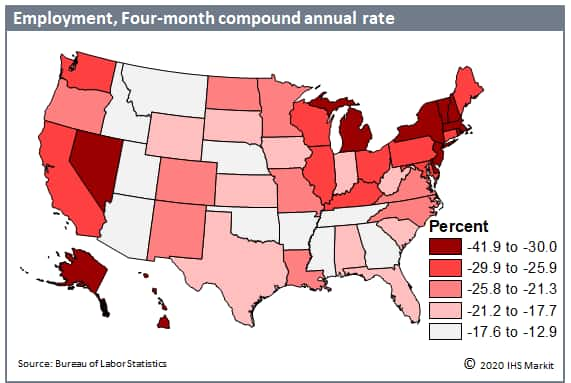
- Despite positive news of early recovery, looking at the
four-month compound annual growth rate from February to June shows
which state economies have fared the worst since the beginning of
the pandemic. States that were hit hardest included those that were
the epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak in the Northeast, such as
New York, New Jersey, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island. Tourism and
travel-reliant states such as Hawaii and Nevada, and heavily
goods-producing midwestern states such as Michigan, also sustained
heavy blows. All these states declined in employment at an annual
rate of at least 30% over the four-month period. As we expected,
the states that fared the best are smaller states with rural
geographies that naturally allowed for better social distancing,
such as Utah, Idaho, and Arizona. While some of these states
enjoyed less restrictive quarantine measures during the outbreak,
some also benefited the least from the recovery in June. (IHS
Markit Economist Steven Frable)
- Aurora Innovation is expanding its testing and development of commercial autonomous vehicles (AVs) to the US state of Texas, according to a company announcement via a blog post on 20 July. The announcement states that Aurora will add a fleet of Chrysler Pacifica minivans and later Class 8 trucks, testing AVs on commercial routes along key logistics delivery corridors in the US state. Aurora also states that the fleets will be fully integrated with the company's new FirstLight Lidar. Aurora says that the amount of freight moved along Texan highways is expected to nearly double over the next 25 years, although it does not indicate the source of that forecast. In addition, the company has confirmed that its first commercial AV product will be launched in the trucking sector, "where the market is largest today, the unit economics are best, and the level of service requirements is most accommodating". Although Aurora has outlined its plans to expand its AV testing, it has not said how many vehicles will be in its Texan fleet or when it is expecting to achieve commercialization. Aurora was established by former Google executive Chris Urmson and has signed deals with several automakers, including Hyundai and Fiat Chrysler Automobiles. However, a proposed deal to work with Volkswagen (VW) was cancelled ahead of VW's investment in Argo AI and partnerships with Ford. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Ford and Intel's Mobileye have formed a partnership aimed at improving the camera-based detection capabilities of driver-assistance systems, including collision avoidance. Meanwhile, Ford has appointed a new general counsel and a new purchasing vice-president. Under the new partnership with Ford, Mobileye will provide its suite of EyeQ sensing technology to support Ford's existing Co-Pilot360 driver-assistance features. This technology will include Mobileye's EyeQ computer chips and software to help identify precisely what the windshield camera sees. Ford says the Mobileye technology will support lane-keeping, automatic high-beam headlights, pre-collision assistance with automatic emergency braking, and intelligent adaptive cruise control features. Ford also will use the technology to support its upcoming active driver assistance technology. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- PetMed Express has highlighted continued buoyancy in the US companion animal sector by posting a 20% sales upturn during its fiscal first quarter. For the quarter ended June 30, sales reached $96.2 million. The firm benefitted from higher reorders, more first-time customers and increased average order size, as pet owners increasingly adopt online spending habits. Reorder sales were up 19% to $80.4m, while new orders came to $15.8m (+29%). PetMed gained around 186,000 new customers in the quarter. This is compared to 140,000 new customers in the same period of 2019. The average order size for the latest quarter was $89, compared to $86 at this point last year. Delray Beach, Florida-based PetMed said net income for the quarter was $7.8m - up slightly on the $5.3m posted this time last year. (IHS Markit Animal Health's Joseph Harvey)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Most European equity markets closed higher today; Germany +1.0%, Italy +0.5%, Spain/France +0.2%, and UK +0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; UK -2bps, Italy -1bp, Germany flat, and France/Spain +1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -2bps/58bps and iTraxx-Xover -5bps/341bps.
- Brent crude closed +2.4%/$44.32 per barrel, which is its best close since 6 March.
- The unusually long meeting of the European Council over the
last few days finally secured an agreement on the recovery fund,
modifying the preliminary arrangements announced by the European
Commission in June. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- As highlighted previously, the fanfare accompanying the announcement reflects three key aspects of the agreement: its scale, and the methods of funding and distribution. In broad terms, they all still apply to the modified deal, though there have been some significant amendments.
- In brief, the European Commission will use its AAA rating to borrow EUR750 billion in total, to be distributed across the EU member states. EUR390 billion will be disbursed in the form of grants (down from the initial proposal of EUR500 billion), with EUR360 billion in the form of loans (up from the initial EUR250 billion).
- To be eligible, EU member states will need to prepare national recovery and resilience plans setting out their reform and investment agendas for the years 2021-23. These will assessed by the Commission on the basis of consistency with the objectives of strengthening growth potential, job creation and economic and social resilience, along with contributions to the EU's green and digital transition agenda. Approval by EU member states will be via Qualified Majority Voting.
- EUR313 billion of grants and EUR360 billion of loans will be disbursed via the main Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF), with the rest distributed through a variety of smaller programs. In 2021-22, 70% of the grants provided by the RRF will be disbursed, with the remaining 30% to follow by the end of 2023.
- RRF grant allocations for member states will be determined primarily by historic unemployment rates and COVID-19 virus-related GDP losses. Overall, under the new proposals, as before, Italy, Spain and some emerging European countries including Poland are set to be the main beneficiaries.
- Due to opposition from a handful of member states - Austria, Denmark, the Netherlands and Sweden (which became known as the "frugal four") - various adjustments had to be negotiated, leading to the exceptionally long duration of the meeting of the European Council.
- In addition to the change in the split between grants and loans, the four member states also secured increases in their rebates from their contributions to the EU budget. Another notable change was the introduction of an "emergency brake" to halt transfers if a member state is considered not to be fulfilling its reform objectives. The brake is time limited at three months, however, with the ultimate decision in the hands of the Commission. Disbursements will also be linked to observing the rule of law, a particular focus for Poland and Hungary.
- In order to secure an agreement, some elements of the "New EU" agenda were dropped, including a proposed solvency instrument to aid recapitalization of struggling companies.
- There was also a large reduction in the proposed budget for the "Just Transition Fund", which has the goal of lowering the cost to lower-income member states of reductions in carbon emissions.
- The UK's central government finances are displaying
considerable stress from the COVID-19 virus crisis. Substantial
fiscal costs are resulting from the public health measures and
policies to support businesses and households. (IHS Markit
Economist Raj Badiani)
- Chancellor of the Exchequer Rishi Sunak has revealed that direct spending to combat the COVID-19 virus crisis had risen to GBP158.7 billion (USD200 billion). Including the new measures announced in his summer statement, direct spending will rise to GBP190 billion, or around 9.5% of nominal GDP (estimated at GBP1.9876 trillion in 2020).
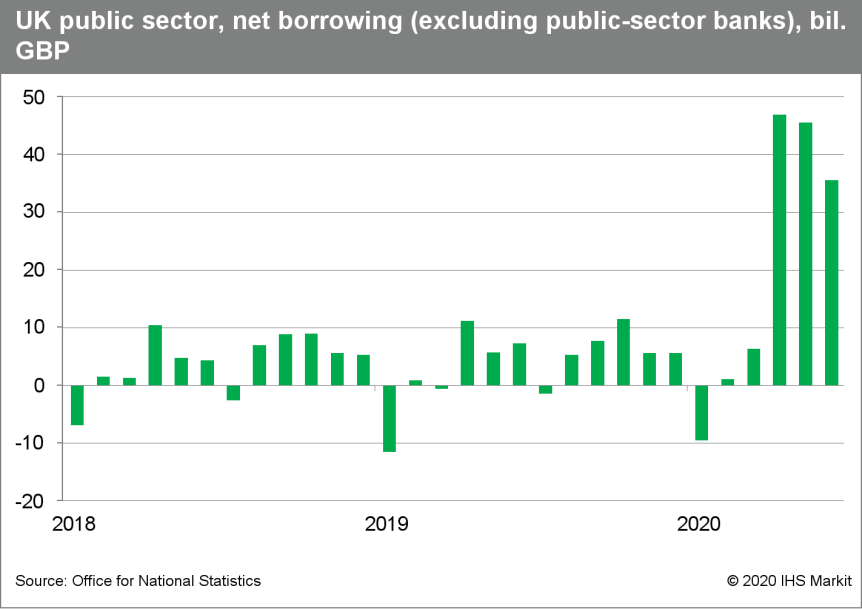
- According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), UK government borrowing (public-sector net borrowing excluding public-sector banks; PSNB ex) stood at GBP35.2 billion in June, which was GBP28.3 billion higher than a year earlier (see first chart below).
- Encouragingly, the borrowing estimate for May has been revised down by GBP9.8 billion to GBP45.5 billion, in line with higher calculations for tax receipts and National Insurance contributions.
- Nevertheless, in the first three months of the current fiscal year (FY; three months to June), government borrowing was GBP127.9 billion, up from GBP24.7 billion a year earlier.
- Central government receipts collected by HM Revenue & Customs fell for the fourth month in June, declining by 20.1% year on year (y/y), pulled down by shrinking economic activity, job losses, and companies deferring tax payments.
- VAT cash receipts continued to plunge in line with the
government's VAT payment deferral policy, allowing firms to delay
their VAT payments due between 20 March and 30 June to early 2021
(before 31 March 2021). In June, VAT cash receipts plunged by 86.4%
y/y to GBP1.1 billion.
- Swiss Federal Customs Office data reveal that nominal,
seasonally and working-day adjusted exports rebounded by 6.9% month
on month (m/m) in June, after -0.9% in May and -12.6% in April.
Imports increased 7.3% m/m in June, following a sharp initial
increase of 10.5% already in May but a much larger plunge in April
(-21.9%). (IHS Markit Economist Timo Klein)
- In year-on-year (y/y) terms, exports at -15.1% are now broadly on a par with imports at -15.7%, having outperformed in recent months.
- The seasonally adjusted trade surplus has edged up slightly from May's CHF2.7 billion to CHF2.8 billion in June, which is well below April's all-time high of CHF4.1 billion but only moderately smaller than the surplus of CHF3.2 billion in June 2019. The picture is somewhat less favorable in price-adjusted terms, however, as June's deficit of CHF0.5 billion compares to the previous month's -CHF0.8 billion and just -CHF0.1 billion in June 2019.
- The sector breakdown for price-adjusted exports in June - total at 7.9% m/m - reveals that chemicals/pharmaceuticals, Switzerland's largest export sector by far (encompassing more than half of total exports), underperformed at 3.2% m/m. There was a similar underperformance in May, but this reflects the very elevated base created by a much-better-than-average performance of the sector during January-April. The sector's second-quarter dip of -5.0% q/q was thus much more limited than for overall exports (-12.5%).
- In June alone, the driving factors for the export recovery were precision instruments (17.3% m/m), watches (39.4%), and jewelry (195.5%).
- The breakdown for real imports was similar: an overall increase of 5.5% m/m was driven by vehicles (58.2% m/m), precision instruments (9.1%), and jewelry (43.6%; this is a relatively small sector, however). By contrast, deliveries to the chemical/pharmaceutical sector posted -4.4% m/m, though - as in the case of exports - following outperformance during January-April.
- The most conspicuous aspect of the export breakdown by region (only available in nominal terms; total at 6.9%) was the strong rebound to Asian destinations (19.4% m/m), with exports to China (21.3%) even surpassed by those going to the Middle East (37.3%), Singapore (39.5%), and India (27.0%).
- Exports to the EU were close to the overall average at 7.1% m/m, whereas those destined for North America (US and Canada) only increased by 3.2%.
- Switzerland-based private equity firm Partners Group has agreed to acquire a major equity stake in Portuguese crop input company Rovensa from private equity group Bridgepoint. Rovensa is a provider of crop protection, biopesticide and biostimulant products. The transaction values the company at an enterprise value of around €1 billion ($1.1 billion). Following the investment, Partners Group will work closely with Rovensa's management team, led by chief executive officer Eric van Innis, on several key strategic initiatives, including the accelerated development of the company's biological solutions portfolio, the continued "internationalization" of the company, and select further acquisitions to continue to build its capabilities. In addition, Partners Group plans to continue to support the company's research and development culture, focusing on high-growth market niches. (IHS Markit Crop Science's Sanjiv Rana)
- Renault Group has revealed that its global sales have fallen by
more than one-third during the first half of 2020 as the COVID-19
virus pandemic had a significant impact on its performance. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- According to data released by the automaker, group demand retreated by 34.9% year on year (y/y) to 1,256,658 units during the six months ending 30 June. Of this total, passenger car sales fell 35.9% y/y to 1,031,081 units, while light commercial vehicle (LCV) sales contracted at a slightly lower rate of 29.8% y/y to 225,577 units.
- At a brand level, sales of the group mainstay Renault brand fell 37.9% y/y to 760,299 units, while Dacia sales dropped 46.2% y/y to 211,158 units.
- Sales of the predominantly Russian Lada brand also retreated by a higher rate of 23.3% y/y to 152,714 units.
- Combined sales of its Jinbei and Huasong brands from its Chinese partnership with Brilliance declined by a relatively modest 10.5% y/y to 70,125 units, as deeper losses in its local market during earlier months from the COVID-19 virus have been caught up in recent months.
- However, the group brands' results were not all negative. Sales of the South Korea-only Renault Samsung brand have grown 58.8% y/y to 53,142 units thanks to the launch of the new XM3, which is sold as the Renault Arkana in other global markets, while there was also some support to the results from the QM6 as well, following big revisions to its offering.
- The disbanding of a joint venture (JV) between General Motors (GM) and AvtoVAZ means that Renault Group now includes the Chevrolet Niva - now sold under the AvtoVAZ brand - as part of its global sales, with 8,520 units sold since the beginning of the year.
- In its core European region, its light-vehicle sales fell by 41.8% y/y to 623,854 units, with a 36.1% y/y fall to 242,534 units suffered in the French market alone, although its performance in June has been helped by newly introduced market incentives.
- Another region where it has suffered steep declines is the Americas, where the group largely focuses on South America. In this region, Renault's sales tumbled by 44.7% y/y to 113,826 units, as its performances in Brazil, Argentina and Colombia helped dragged it backwards at this rate.
- In the Africa, Middle East, India and Pacific region, Renault's sales dropped 30.8% y/y to 150,734 units, as while sales jumped by 51.3% y/y to 55,242 units in South Korea on new models, there were significant losses in other markets, including India, Morocco, and Algeria.
- The company will announce how great the financial impact on its business has been when it reveals its first-half 2020 results on 30 July. However, the company is already looking at a more positive second half of the year. It has already felt some benefit from the incentives being introduced by some governments in Europe to revitalize demand.
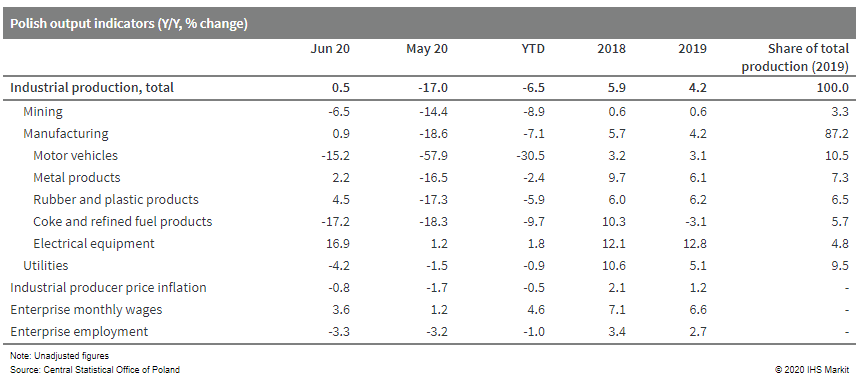
- On a seasonally adjusted basis, Polish industrial production
increased by 9.7% month on month (m/m), after 12.2% m/m growth in
May. However, seasonally adjusted output in June remained 4.9%
lower than in June 2019. (IHS Markit Economist Daniel Kral)
- On a seasonally unadjusted basis, Polish industrial output in June was 0.5% higher year on year (y/y). This was driven by a positive calendar effect with two more working days in June and a positive base effect, as June 2019 was especially weak.
- Among the main sub-groups, output in durable consumer goods increased by 16.2% y/y, intermediate goods by 3.5% y/y, and non-durable consumer goods by 3.3% y/y. Energy and capital goods declined by 9.9% y/y and 8.6% y/y, respectively.
- On a seasonally unadjusted basis, 21 out of 34 industrial divisions increased in June compared with June 2019. Among them, the biggest increases were recorded in the manufacture of furniture, up by 19.3% y/y, and wood products, up by 17.6% y/y, as well as the manufacture of electrical equipment, up by 17.6% y/y.
- On a monthly basis, the largest increases were recorded in the manufacture of motor vehicles, up by 80.2% m/m; the manufacture of leather and related products, up by 37.2% m/m; and the manufacture of furniture, up by 33.4% m/m.
- Despite the strong bounce back in industrial activity, enterprise employment in June shrunk by 3.3% y/y. The large increase in monthly wages may be related to lower paid jobs being cut first, resulting in higher average wages.
- In a separate release, retail sales in June were 8.1% higher than in May on a seasonally adjusted basis. Compared with June 2019, retail sales were down by 1.3% (or 1.9% in nominal terms).
- Among retail sales sub-components, the largest growth was
recorded in furniture, radio, TV, and household appliances, up by
16.1% y/y (consistent with the outperformance of the industry
division), and newspapers and books, up by 6.1% y/y.
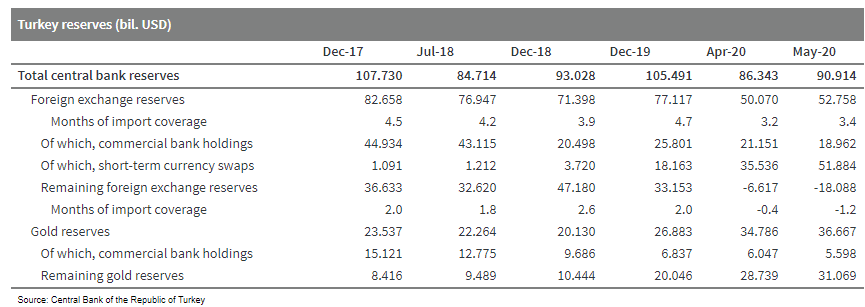
- On 18 July, the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey (TCMB)
raised its foreign-currency reserve requirements by 300 basis
points across all liability types and maturity brackets for all
banks. The Bank estimated, in its press release announcing the
move, that it would withdraw USD9.2 billion of foreign-currency and
gold liquidity from the market. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew Birch)
- The TCMB also pointed out that it had initially dropped its foreign-currency reserve requirements by 500 basis points on 17 March, releasing USD5.1 billion of liquidity at the time to support credit operations at the height of the financial crisis triggered by the rapid global spread of the COVID-19 virus.
- In a secondary move, the TCMB has reportedly also now raised charges on commercial banks' foreign currency deposits. This action would thus push commercial banks to either reduce the interest rates paid for foreign currency deposits or even start charging for those deposits according to former TCMB governor Durmus Yilmaz.
- The resulting action would push households and/or non-financial institutions to either hold their hard currencies outside of the banking system or convert their holdings to lira - the likely targeted goal of the action as it would relinquish more hard currency to the banks to subsequently turn over to the state.
- Although the TCMB, in its press release, is presenting the
reserve requirement increase as a measure to normalize the
financial system and support financial security, it is likely more
targeted at rebuilding depleted official foreign currency reserves.
Defense of the lira has severely undermined official foreign
currency reserves.
- Estonia-based ride-hailing firm Bolt has launched a low-cost service called Bolt Go in 35 South African cities. The company claims that Bolt Go fares will be approximately 20% cheaper than those of the regular Bolt rides. The service will allow drivers to use hatchback cars to serve riders in the country by accessing the Bolt platform. The Bolt Go service will include the company's existing Trip Protection, a no-cost, value-added insurance product that covers all passengers and drivers in case of an accident. Gareth Taylor, country manager of Bolt South Africa, said, "Smaller hatchback cars are less expensive to purchase, have lower maintenance costs, and are more fuel-efficient to operate than Bolt's regular larger sedan cars. These lower operational costs also enable Bolt Go fares to be significantly more affordable." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed higher across the region; Australia +2.6%, Hong Kong +2.3%, India/South Korea +1.4%, Japan +0.7%, and China +0.2%.
- Japan's Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 0.1% from a month
earlier on a seasonally adjusted basis in June, and year-on-year
(y/y) growth also remained at 0.1%. The CPI, excluding fresh food
(core CPI) - a reference series for the Bank of Japan (BoJ) - also
rose by 0.1% month on month (m/m) and moved up to the year-earlier
level following two consecutive months of deflation. The CPI,
excluding food and energy (core-core CPI), also increased by 0.1%
m/m, and y/y growth continued to rise at 0.4%. (IHS Markit
Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- Although declines in energy prices and day-care/preschool fees were major factors behind sluggish inflation, weaker increases in fresh food were offset by softer declines in gasoline and electric charges.
- The shift to stay-home/working-from-home lifestyle lifted demand for home electronics and helped lift prices of household durable goods and mobile phone communication charges, these were largely offset by larger declines in accommodation fees.
- The June results reflected mixed effects of the COVID-19 virus pandemic, but Japan's CPI is likely to remain weak over the near term because of downbeat outlooks for global oil prices and sluggish domestic demand.
- Business re-openings could help a recovery of demand, discount sales of out-of-season goods, declines in wages because of lower working hours and performance-linked bonuses, and social distancing practices will continue to weigh on prices.
- After reporting zero confirmed cases for 14 consecutive days,
Beijing lowered its emergency response back to third level on 20
July, after raising it to second in mid-June. Large scale testing
efforts helped to stop the local new case count at a 335 during
this "second wave" of outbreak. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Eased restrictive measures enable a range of offline activities to resume, including reopening indoor sports and entertainment venues such as museums and theaters, organizing trans-provincial group tours, and holding events with up to 500 people. Quarantine measures will only be imposed on those traveling from abroad or from domestic areas with medium to high infection risks.
- In particular, the commerce department of Beijing will re-launch the shopping festival that was suspended due to the recent case surge. Local government plans to introduce various promotions to boost holiday shopping, night economy, and online sales.
- As of 16 July, work resumption rate in Beijing had basically returned to levels seen in early June. Nearly 100% of major office buildings, large construction sites, large industrial enterprises and large supermarkets have resumed work; while catering businesses slightly lag behind, with their work resumption rate reaching 91.1%, 1.8 percentage points lower than before the recent outbreak.
- China's ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing (DiDi) is considering an initial public offering (IPO) by this year end, reports Pandaily. According to the report, the company plans to be listed in Hong Kong and is seeking valuation of more than HKD600 billion (USD80 billion). DiDi has over 31 million drivers registered on its platform and has attracted 550 million customers, who are using the company's range of app-based transportation options. DiDi is strengthening its presence in markets beyond China and has formed a global ride-sharing partnership network with Grab, Lyft, Ola, Uber, 99, Taxify, and Careem, in countries covering over 80% of the world's population. The company has tapped many markets worldwide by either launching its own services or investing in local ride-hailing firms. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility)
- Heirs of Samsung Electronics and Hyundai Motor Group have discussed their planned collaboration in the electric vehicle (EV) and mobility businesses, reports Yonhap News Agency. The companies' de facto leaders Lee Jae-yong of Samsung and Chung Euisun of Hyundai Motor have met officially to discuss future mobility technologies at Hyundai's research and development (R&D) center in Namyang (South Korea). Lee was accompanied by Kim Ki-nam, vice-chairman of the semiconductor division; Jun Young-hyun, CEO of Samsung SDI; Kang In-yup, president of System LSI; and Hwang Sung-woo, president of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology. Samsung executives were briefed on Hyundai Motor's technologies and products related to urban air mobility and robotics and drove Hyundai's autonomous vehicles (AVs) and hydrogen-powered cars. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Since the start of 2020, Bank Indonesia (BI) has lowered the
seven-day reverse repurchase (repo) rate by 100 basis points in a
bid to shore up economic growth. According to post-decision
statements from BI, the Board of Governors decided that the
decision to cut was consistent with low inflation and sustained
external stability, with the rupiah trading closer to
IDR14,400-14,800/USD1 since the start of July versus the
IDR16,600/USD1 hit in late March. (IHS Markit Economist Bree Neff)
- According to statements by BI Senior Deputy Governor Destry Damayanti on 20 July, the central bank now expects a "U"-shaped recovery because of the continued rise in COVID-19 infections and the expectation that virus containment measures cannot or will not be fully removed for some time.
- According to Damayanti, BI expects real GDP to contract between 4.0% year on year (y/y) and 4.8% y/y for the second quarter. IHS Markit's forecast is for contractions on the order of 4.2-4.8% y/y for the second, third, and fourth quarters of 2020 implying a potentially extended U-shaped recovery.
- Following the decision, BI Governor Perry Warjiyo has indicated that further easing will depend on inflation, which came in at a 20-year low of 1.96% y/y in June as domestic demand remained soft, with core inflation also sinking to a survey-low of 2.3% y/y.
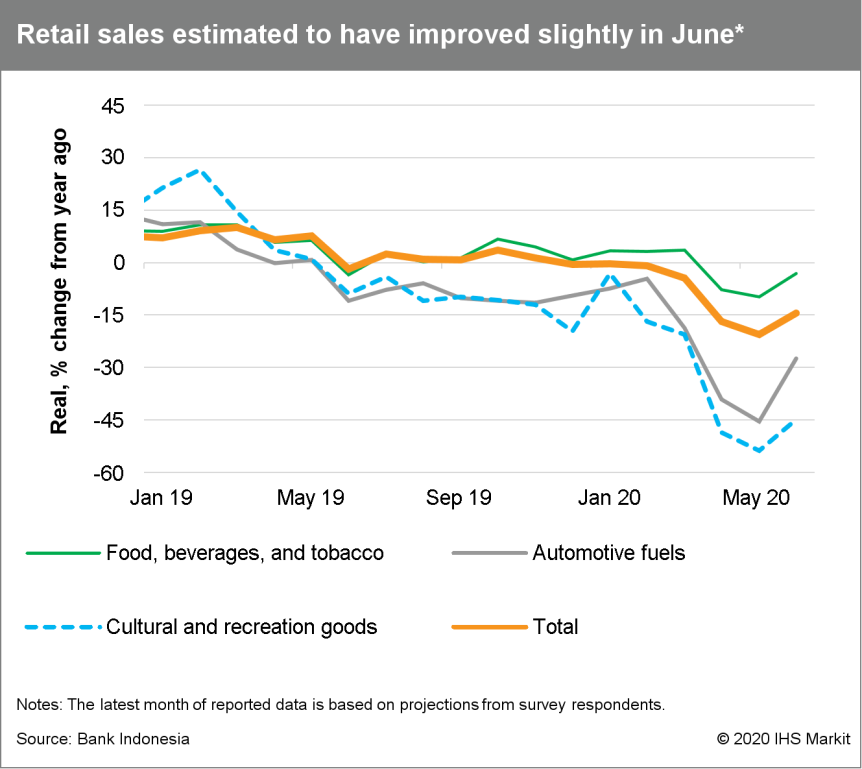
- Continued weakness implied in estimated June retail sales data also points to softness in demand, as well as inflation.
- The central bank's stated openness for further easing leaves
the door open to further conventional monetary easing via the
policy rate, but IHS Markit remains concerned that it will not take
too much for financial markets to be roiled by risk aversion.
Therefore, we expect at most BI could get away with cutting the
policy rate by another 50 basis points, but we assess that one more
cut of 25 basis points is most likely and will be complemented by
the continuation of BI's other macroprudential and quantitative
easing programs.
- There is a call to develop variety of dairy products other than cow milk and the rise of camel milk is part of the growth story in China. Camel milk powder remains a small category and there is no HS code allocated yet. According to Xinhua Net (June 27), Kazakstan's camel milk has recently made an official entry into China. A factory, owned by Eurasia Investment Co Ltd, based in the central Kazakhstan's Karaganda region produces camel and horse milk, with an annual output of 60 tons of each. The raw material is from their own 200 camels and 2,500 horses. The factory is planning to increase the output to 200-300 tons per annum. On January 29, China's General Administration of Customs granted the factory an export license. Three Kazakh enterprises producing camel dairy products, including Eurasia Invest, are among the first batch of companies to receive export licenses. However, they have yet not obtained an export license for horse milk to China. Sales are made through e-commerce to Chinese consumers directly. Kazakhstan's Ministry of Agriculture reported (June 17) that the country produced 423 tons of horse milk in H1 2020, up by 17% over the year before. In 2019, the country produced 1,103 tons. In the same period, it produced about 1,000 tons of camel milk. In 2019, total production was 3,177 tons, up by 45%. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Hope Lee)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-21-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-21-july-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+21+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-21-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 21 July 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-21-july-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+21+July+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-21-july-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




