Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Dec 14, 2020
Daily Global Market Summary - 14 December 2020
Most European equity markets closed higher, while the US and APAC markets closed mixed. US government bonds closed flat and the US dollar was lower, while benchmark European bonds were mixed across the region. European iTraxx credit indices closed modestly tighter across IG/high yield and CDX-NA indices closed flat and at the widest levels of the day. Oil closed higher, gold/silver lower, and copper was flat. The US electoral college officially confirmed Joe Biden's presidential victory, while at the same time, the country began administering the first round of COVID-19 vaccinations as the number of hospitalizations continues on a concerning trajectory.
Americas
- US equity markets closed mixed and near the lows of the day; Nasdaq +0.5%, Russell 2000 +0.1%, S&P 500 -0.4%, and DJIA -0.6%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed flat/0.90% yield and 30yr bonds flat/1.63% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/54bps and CDX-NAHY -1bp/304bps. CDX-NAHY
was as tight as -10bps at 8:00am EST but began to widen 30 minutes
later.
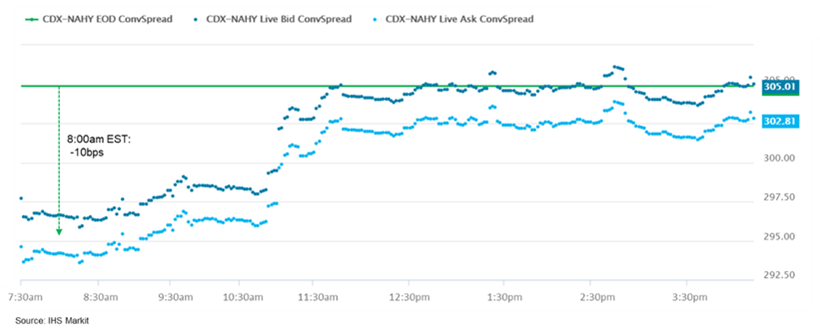
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.3%/90.71, but was as low as 90.43 at 8:57am EST and increased +0.5% from the day's low by 10:59am EST.
- Gold closed -0.6%/$1,832 per ounce, silver -0.2%/$24.05 per ounce, and copper flat/$3.53 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +0.9%/$46.99 per barrel.
- The first U.S. COVID-19 vaccinations outside of clinical trials began Monday, kicking off the most urgent mass immunization campaign since polio shots were rolled out in the 1950s. A nurse in New York was among the first to receive the shot, and health workers throughout the U.S. were also set to receive the newly authorized vaccine developed by Pfizer Inc. and BioNTech SE. Pfizer shipped vaccine vials out Sunday, and hospitals and health departments across the country received them early Monday. A total of 55 sites nationwide had received vaccine shipments by around noon on Monday, said Gen. Gustave Perna, chief operation officer for Operation Warp Speed, the U.S. government's coronavirus-response program. (WSJ)
- Joe Biden officially clinched the presidency after the Electoral College confirmed his victory Monday, capping a tumultuous period sparked by Donald Trump's refusal to acknowledge he lost with the help of Republicans willing to support his unsubstantiated claims. (Bloomberg)
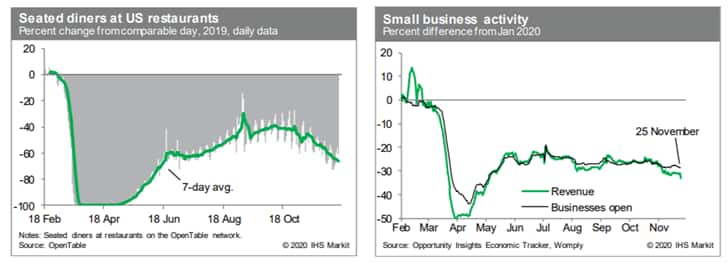
- The count of seated diners on the OpenTable platform (relative
to year-earlier levels) has continued to trend lower. The average
over the last seven days was the worst since June, as many states
and locales have tightened restrictions on indoor dining and
cooling temperatures are limiting opportunities for outdoor dining.
Meanwhile, revenues at small businesses and the count of small
businesses open both deteriorated over November, with revenues over
the seven days ending 25 November at the lowest level since early
May. (IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
- Arkema has agreed on the proposed sale of its polymethyl
methacrylate (PMMA) and methyl methacrylate (MMA) business to
Trinseo for an enterprise value of €1.137 billion ($1.381 billion),
after announcing in April that it was considering divesting the
business. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The sale is "fully in line with Arkema's ambition to become a pure specialty materials player by 2024," the company says. The offer values the PMMA/MMA business at 9.3 times its estimated 2020 EBITDA, it says. The deal, subject to approval by the relevant antitrust authorities and to an information and consultation process involving Arkema's employee representative bodies, is expected to be finalized by mid-2021, it adds.
- The business to be sold employs about 860 people and operates seven production sites, with four located in Europe (two in Italy, one each in France and Denmark) and three across the US and Mexico. In the US, Arkema has an MMA-capacity-reservation agreement with Dow. Sales of the business in 2020 are estimated at about €510 million, with EBITDA of about €122 million, according to Arkema. In 2019, EBITDA was close to an historic high for the business at €160 million, Arkema says.
- The deal, if it proceeds to completion, would mark Trinseo's entry into the PMMA/MMA business, where Arkema is one of the leading PMMA producers, competing with Mitsubishi Chemical, Röhm, and Sumitomo Chemical. The overall PMMA market was estimated at 2 million metric tons in 2018.
- Trinseo, which also announced today it is exploring the potential divestment of its synthetic rubber business, says the Arkema transaction is expected to generate approximately $50 million in annualized pretax cost synergies by 2023 and additional revenue synergies by leveraging Trinseo's market overlap and existing Asia organization to accelerate growth. It also expects to realize an additional $25 million in IT-related productivity savings in its existing businesses as a result of harmonizing global ERP systems. "These IT-related savings represent meaningful benefits above the PMMA-related synergies," Trinseo says.
- Arkema's PMMA business is a leader in several end-market applications including automotive and building and construction, and will enhance Trinseo's existing strong positions in these applications, Trinseo says. The combination of Trinseo's existing portfolio with the PMMA business "will enable greater focus on future growth markets such as Asia, which represents approximately 70% of the global PMMA market," it adds.
- SBC Securities and Deutsche Bank Securities (DBS) served as lead financial advisors to Trinseo on the PMMA business acquisition, with DBS and HSBC providing committed debt financing in support of the transaction. Centerview Partners served as strategic advisor and Kirkland & Ellis served as primary legal advisor to Trinseo.
- There has been a sharp increase in Florida's orange box tax, which is a levy on every box of citrus harvested in the state used to promote Florida orange juice. The rate has just been increased to 12 cents per box from seven cents/box, following a vote passed by six to three by the Florida Citrus Commission. Grapefruit and specialty fruits will remain at seven cents/box. The vote Wednesday also required up to USD1.0 million to be shifted from daily operations of the Florida Department of Citrus (FDOC) to the marketing campaign. In June, the FDOC based revenue projections for the 2020-21 growing season on production of 67.65 million boxes of oranges, 4.89 million boxes of grapefruit and 1.02 million boxes of specialty crops — mostly tangerines and tangelos. However, this month's USDA forecast was for 57 million boxes of oranges, 4.5 million boxes of grapefruit and 1.1 million boxes of other crops. Without the increase in the box tax, this would have cut over USD1.1 million from the FDOC's projected revenue of USD19.875 million in the current fiscal year. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Neil Murray)
- Electric commercial vehicle companies Lightning eMotors and Electric Last Mile Solutions have both announced plans to go public in 2021 through mergers with special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs), also known as reverse mergers. Lightning eMotors announced its plan to go public on 10 December and said it would be working with a company called GigCapital3, a technology, media and telecom private-to-public equity (PPE) corporation. Following the merger, Lightning eMotors intends to list the new version of the company on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), using the stock ticker ZEV. The SPAC merger deal is due to be closed in the first half of 2021. The combined company will be called Lightning eMotors Inc. Lightning eMotors is a commercial medium-duty electric vehicle (EV) company, with proprietary vehicle control software, EV chassis integration software and analytics, and customised products including DCFC mobile-charging solutions. The company says it has the leading market share in Class 3-7 zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs) and is the only manufacturer with a full line of battery and fuel-cell zero-emission commercial vehicles on the road. The GigaCapital3 transaction is supported by USD125 million in equity and convertible financing through a private investment in public equity (PIPE) transaction, which includes BP Technology Ventures in its investors. Lightning eMotors expects the transaction to add more than USD270 million to its balance sheet. These two announcements add to the list of automotive SPAC merger deals announced in 2020, many focused on electric vehicle (EV) companies or tech suppliers. Lightning eMotors has a track record in the medium-heavy sector, but ELMS remains unproven. Each company targets specific use cases and sectors of the commercial vehicle industry. A shift to online purchasing and greater demand for delivery services has accelerated drastically as the United States (and the world) is working its way through the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, this is occurring at the same time as regulatory pressures for low- or zero-emission vehicles continue to increase. This combination is creating increased potential in the commercial vehicle sector for ZEVs, and companies are rapidly working to meet the expected demand. Whereas range anxiety and charging infrastructure remain issues slowing consumer adoption of ZEVs, in the commercial sector, the duty cycles of local delivery vehicles overcome those issues, as well as bring the benefits of zero emissions and quiet operations. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Tesla will idle production of the Model S and Model X from 24 December to 11 January 2021, according to CNBC. The source quotes an internal email that it said was sent to production workers on 11 December to announce the temporary shutdown. Employees will be paid for one week and for some holidays but are also expected to take about five of the days as unpaid leave. CNBC published the text of the email and said that Tesla said there will be limited paid opportunities for the affected workers to support other areas of production or volunteer for customer deliveries during some of the time off. In addition, it reports that Tesla CEO Elon Musk sent a separate email to all employees saying that the company needs "to increase production for the remainder of the quarter as much as possible", and that the company has "quite a bit higher" demand than production for the quarter. Tesla has reported, along with its third-quarter results, that global deliveries of the Model S and Model X had declined by 13% in the third quarter, compared with the third quarter of 2019, although production had increased by 4%. In the United States, the Model S accounted for 8.9% of US registrations from January 2019 through to October 2019 and the Model X for 10.1%; for the equivalent period of 2020, the Model S's share dropped slightly to 7.3% of Tesla registrations and the Model X to 10.0%. With no comment from Tesla on the production schedule, there is no indication of what, if anything, it plans for the manufacturing lines. The Model S and Model X are produced only at the automaker's Fremont, California, facility; there are no reports of production slowing at its China facility or for the Model 3 and Model Y production lines. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
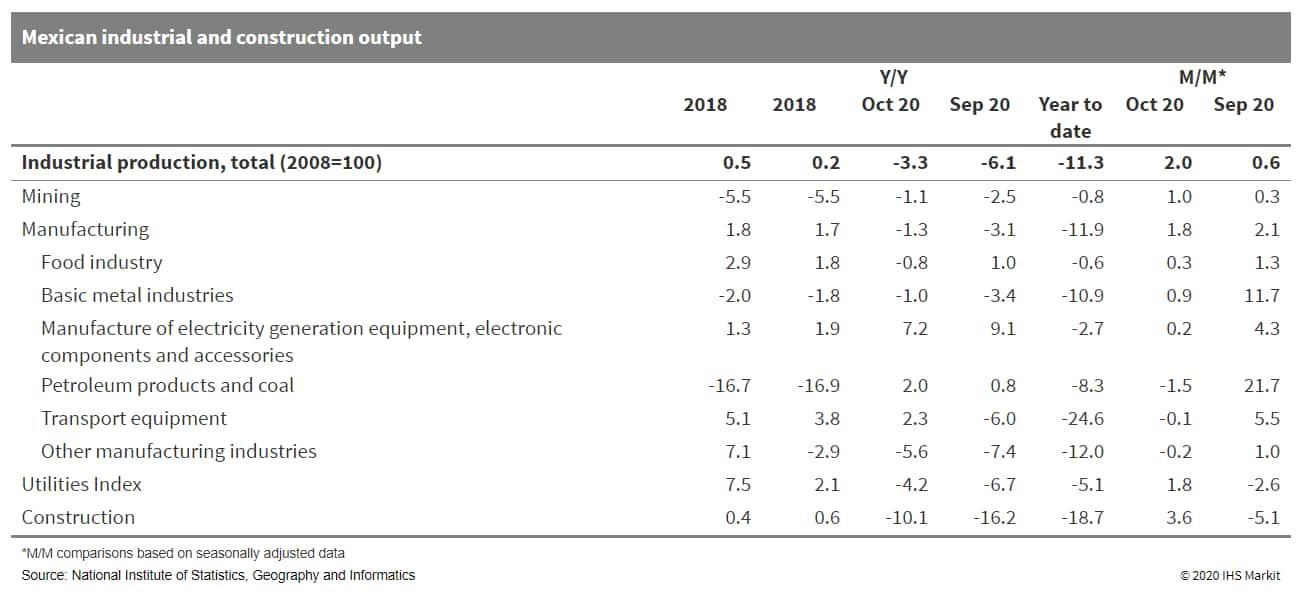
- Mexico's National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI)
reports that industrial production grew by 2.0% in October compared
with September, marking the fifth consecutive month of expansion.
This is based on seasonally adjusted data. INEGI revised its
September figures upwards for growth from 0.0% to 0.6%. (IHS Markit
Economist Rafael Amiel)
- The fastest growth rate was in construction, although the all-important manufacturing sectors expanded almost at the pace of the whole industry.
- In an annual comparison with pre-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-virus pandemic levels, manufacturing shows full recovery, while the other sectors are lagging behind. There is stronger growth in the production of export-driven products such as electronics, automobiles, and other transport equipment as demand from the United States has increased significantly.
- Domestic demand for automobiles is recovering, but is still well behind pre-pandemic levels; in November, it increased compared with October but was almost 25% lower compared with November 2019. Oil production levels have been very flat.
- The outlook for manufacturing is positive: a better economic performance in the US and, thus, stronger demand for Mexican exports will drive growth in 2021. With negotiations on fiscal stimulus now gaining bipartisan support (in the US) and also better prospects that a large amount of the population will be vaccinated by mid-year 2021, the economic outlook for the US has improved.
- Construction in Mexico will continue to be a drag on growth; government investment in infrastructure will still be limited by fiscal austerity, and business sentiment in the private sector will remain subdued as the government continues centralized economic decisions and adheres to a less business-friendly attitude.
- IHS Markit's latest forecast is for Mexico's industrial output
to return to 8.8% in 2021 after plunging by 10.6% in 2020. The 2021
figure may be revised upward given the better US outlook.
- Guatemala's year-on-year (y/y) inflation reached 5.46% in
November following monthly growth of 0.55% between October and
November, reflecting the country's faster-than-expected recovery of
economic activity amid the COVID-19-virus pandemic. (IHS Markit
Economist Lindsay Jagla)
- Guatemala has experienced only two months of negative inflation in 2020 - in January and February - despite lower demand because of the pandemic and low oil prices.
- The primary monthly drivers of inflation were food products (1.18%), housing (0.43%), and restaurants (0.34%). Some of the price increases, especially on agricultural products, can be explained by the destruction caused by hurricanes Eta and Iota in November, which lowered crop supply.
- On the other hand, transportation and recreation experienced the greatest price declines, by 0.31% and 0.17%, respectively. Notably, regular petrol prices continued to decline, by 4.61% month on month in November, which tends to have spillover effects on other prices because of lower transportation costs.
- Guatemala's monthly economic activity index grew in annual terms in both September (0.1%) and October (1.3%), reaching above 2019 levels for the first time since the start of the pandemic.
- Amid low economic activity due to the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries have experienced declines in prices, resulting in inflation rates being well-below target ranges. However, Guatemala's experience has been different, with annual inflation now exceeding the target range of 4.0% ± 1.0%.
- Quicker recovery in terms of economic activity and a less severe economic contraction overall in 2020 have sustained higher levels of demand, causing greater inflation rates. With the monthly economic activity index reaching above 2019 levels in September and October, IHS Markit expects to revise up Guatemala's 2020 GDP forecast to -3.2% during the December round.
- After declining by 42% and 5% in the second and third quarters
of 2020, respectively, Peru's merchandise exports increased by 8%
year on year (y/y) by value (in nominal free-on-board [FOB] terms)
in October, the strongest performance so far in 2020. Imports
remained 13% below 2019 levels. (IHS Markit Economist Jeremy Smith)
- Powered by a strong performance in the mining sector, especially copper and gold, Peruvian exports posted their strongest performance of 2020, rising by 8% y/y, according to Peru's National Institute of Statistics and Information (Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática). Mining products accounted for 59% of Peruvian exports in 2019.
- Strong demand for raw construction materials in mainland China, which imports the overwhelming majority of Peru's copper and is the country's largest trading partner, drove a 22% surge in global copper prices in the third quarter. Prices have since continued to increase, also lifted in part by supply disruption throughout the Andean region. By volume, Peru's exports were down by 9% y/y, underscoring the significant price effect.
- Meanwhile, merchandise imports fell by 20% y/y in the third quarter and remained weak in October. Imports of consumer goods (-8%) were much more resilient than raw materials and intermediate goods (-27% y/y). Peru's trade balance thereby returned to surplus after an anomalous deficit in the second quarter.
- Through the first three quarters of 2020, weak import demand and steep declines in the outflows of private-sector investment income had offset lower foreign-exchange inflows from exports and remittances. IHS Markit forecasts a current-account deficit worth 1.3% of GDP for the year as a whole.
- As of September, mining production was still 11% below 2019 levels; as production recovers, exports by volume will continue to rise, but this will contribute to flattening prices as Peru is second only to Chile in copper production.
- We expect the sol to strengthen to PEN3.56/USD1.00 by year-end on the recent spike in copper prices before largely staying stable in 2021. The Peruvian currency had depreciated to its weakest level in decades amid a turbulent political period in which two presidents were removed from office in the span of a week.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Most European equity markets closed higher except for UK -0.2%; Spain +1.0%, Germany +0.8%, France +0.4%, and Italy +0.3%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -1bp, Spain flat, France +1bp, Germany +2, and UK +5bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/50bps and iTraxx-Xover -8bps/259bps.
- Brent crude closed +0.6%/$50.29 per barrel.
- Millions of Londoners will be ordered to comply with England's toughest coronavirus rules from Wednesday, as U.K. authorities warned a "new variant" of the disease may be driving a rapid rise in cases. Government scientists at the Porton Down military research facility are analyzing the new variant, which Health Secretary Matt Hancock said may be linked to the recent fast spread of infections in the capital. (Bloomberg)
- If a no-deal Brexit is finalized before 31 December, the UK and
the EU would start trading on World Trade Organization (WTO) terms
with various levels of tariffs applying to goods. This could push
up consumer prices for food in general while demand for fresh
consumption may slow down following lower household incomes due to
the pandemic impact. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities'
Hope Lee)
- Trade data shows that the UK imported about USD2.6 billion worth of fresh or chilled vegetables, roots and tubers from the EU in January-November 2020. Tomato imports have the most value at USD412 million cif, followed by cucumbers (USD189 million), mushrooms (USD183 million), cauliflowers (USD157 million) and broccolis, onions and shallots, potatoes and lettuce.
- The Netherlands may feel the biggest impact in a no-deal Brexit as it is the key supplier for many essential vegetables (tomatoes and cucumber). The Dutch account for over half of the total tomato and cucumber import values while Spain accounts for about 25% for tomato and 39% of cucumber.
- The UK tariffs for fresh tomatoes are 8% (1 November-14 May) and 14% (15 May-31 Oct), according to Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board (AHDB). The UK tariff for mushroom is 12% and onions 8%.
- In the winter season, some EU shipments which the UK particularly relies on are carrots (Spain and Italy), tomato (the Netherlands), fennel (the Netherlands, France, Italy), kohlrabi (France and the Netherlands), broccoli (Spain) and pepper (the Netherlands).
- A British fresh vegetable wholesaler told IHS Markit that they are prepared to pass on the extra costs to retailers as the additional costs deriving from transport, tariff and the potentially weakened UK pound would likely squeeze the already low margins.
- According to the Guardian, British supermarkets have been told to stockpile food in anticipation of food shortages due to the no-deal disruption. However, the limited warehouse space will constrain the stockpiling volume of perishable produce.
- Andrew Opie, the director of food and sustainability at the British Retail Consortium, said: "Retailers and suppliers are doing everything they can to reduce disruption for consumers, including increasing the stock of non-perishable items and looking at alternative supply routes."
- However, distant countries of origin may pose additional logistical risks. New suppliers may not always meet the UK's food standards.
- Volta Trucks has announced that it has received an order for 1,000 refrigerated variants of its Zero battery electric truck from Petit Forestier Group. According to a company statement, as part of a multi-year deal, the first refrigerated Zero will begin user testing in 2021 ahead of the start of production in 2022. The vehicles will be equipped by Lecapitaine, Petit Forestier Group's industrial subsidiary, which designs and manufactures refrigerated bodywork and has already started collaborating with Volta's technical team. Volta added that this industrial agreement will also cover all its refrigerated vehicles. This is the latest order contract to be signed by Volta for its Zero model, after it signed a deal with Drinks Cubed in September, followed by trial programs announced with Datashred and Lenham Storage. The latest deal is both the largest and the most important one so far, as it will result in Volta being able to offer customers a modification that is important for the transportation of foodstuffs but can pose a challenge with regards to emissions of the refrigeration unit. The order for 1,000 vehicles is a small fraction of the 58,000-vehicle fleet that Petit Forestier has at the moment, so there could be some opportunity for it to expand this order in future. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- On 10 December, the International Capital Market Association
(ICMA) published its Climate Transition Finance Guidebook,
describing this as a guide for issuers (rather than a deal-specific
framework). (IHS Markit Economist Brian Lawson)
- It sets out guidance to companies on the "practices, actions and disclosures" needed for potential issuers, both regarding transactions with ESG-specific use of proceeds (Green, Social and Sustainability Linked bonds) and those aligned to wider transition and sustainability-linked goals.
- Four clear areas are highlighted: the issuer's climate transition strategy and governance, its business model and how this impacts the environment, "science-based" targets and pathways for the issuer's climate transition strategy and the transparency of implementation.
- Key components of the strategy are disclosure and review.
- For the former, firms may use their normal reporting channels such as annual reports, "dedicated sustainability reporting", filings and investor presentations.
- The Guidebook suggests this should span a long-term climate goal, aligned with Paris Agreement objectives, interim targets towards this, description of oversight and governance, and evidence of a broader sustainability strategy. This should be complemented by independent review including assessment of the credibility and materiality of its targets established.
- Objectives should be monitored using clearly defined and scientifically measurable reference points.
- ICMA standards are the market reference for Green and Social Bond issuance and were extended this year to cover sustainability-linked debt, which offers greater flexibility over the use of proceeds with firms instead measured against wider ESG objectives.
- The new guidebook extends this further by moving to firm-wide rather than a transactional basis, giving guidelines for companies to conduct their wider ESG strategy.
- The guidebook addresses an important gap in prior ESG issuance: that a firm may have environmentally positive goals regarding a specific financing but fail to match this at a broader corporate level.
- Mercedes-Benz has outlined its production network for its new generation of EQ battery electric vehicles (BEVs) up until 2022, according to a company statement. The EQC has already been produced at Bremen since the first half of 2019. This will be joined by the EQA C-Car BEV, which has already started production at the Rastatt plant in Germany, with its official launch taking place on 20 January 2021. This means that the Rastatt line will run with fully electric models on the same production line as compact vehicles with conventional and hybrid drives. The EQA will also be produced by Mercedes-Benz cars' Chinese joint venture (JV) partner Beijing Automotive (BBAC) in Beijing from 2021 too. This will be joined by the EQB compact crossover, which is the BEV version of the GLB SUV, which will be manufactured at the company's plant in Kecskemét (Hungary) for the world market and by BBAC in Beijing for the local market from 2021. As previously announced, in the second half of 2021, Mercedes-Benz will start production of the EQS full BEV luxury sedan, which Mercedes-Benz describes as an independent, fully electric member in the new S-Class program, at its new Factory 56 digital production location, which will also produce the new S-Class and Mercedes-Maybach S-Class on the same line. In addition the EQE BEV E-Class equivalent in the EQ range will begin production in Bremen in the second half of 2021, followed shortly after that by production in Beijing. The company's plant in Tuscaloosa (US) will also begin production of the EQE in 2022. This announcement is more or less confirmation of previous statements regarding Mercedes-Benz's short- and medium-term BEV production plans with it tallying with IHS Markit's production forecast for the brand. IHS Markit forecasts that Mercedes-Benz full BEV production will increase from 27,000 in 2020 to 221,000 in 2022. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- The sectoral data released by the Russian Federal State
Statistical Service (RosStat) suggests that the 13.0% q/q growth
followed losses of 1.9% in the second quarter and remarkable 18.7%
in the first three months of the year. (IHS Markit Economist Lilit
Gevorgyan)
- RosStat confirmed its earlier estimate of 3.6% year-on-year (y/y) contraction of the real GDP during July-September, following 8.0% y/y decline in the second quarter. The GDP deflator stood at 0.1% in the third quarter. RosStat does not provide quarterly data for the value-added sectors.
- The latest print shows that the manufacturing sector stabilized in the third quarter, following a 7.9% annual decline April - June when Russian manufacturing firms felt the brunt of the anti-pandemic containment measures.
- However, the extractive sector continued to decline during July-September, down by 12.3% y/y, only slightly moderating from 12.8% y/y fall in the second quarter. These persistent losses are a result of around 23% of crude oil production cuts.
- Russia undertook this commitment within the OPEC+ framework in April as part of a concerted international bid to shore up market oil prices after a historic 75% collapse at the global onset of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic.
- Overall, industrial output contracted by 4.8% in the third quarter, although the decline eased compared to the 9.3% y/y fall in the second quarter.
- Services, which make up 60% of the value added, shrank by 2.9% y/y during July-September. This decline moderated from 8.5% y/y fall in the second quarter.
- Agriculture and public administration continued to expand in the third quarter. The increase in the public administration was expected, considering the fallout from the COVID-19 virus pandemic and the high demand for new services.
- Equally, the agricultural sector has benefited from the delayed transmission of the pandemic and increased domestic demand in the wake of external supply chain disruptions.
- Considering the better-than-expected third-quarter results, we have lifted our 2020 real GDP forecast for Russia to a contraction of 4.2% (from a fall of 5.9%). An economic rebound of 2.9% will follow in 2021.
- Already, the fourth quarter had a weak start. According to RosStat, industrial production saw the sharpest fall since July, down by 5.9% y/y in October from y/y contractions of 3.6% in September and 4.2% in August.
- Autonomous vehicle (AV) sensor manufacturer Innoviz Technologies is planning to go public through a merger agreement with Collective Growth Corporation, a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC). This will bring Innoviz's market value to USD1.4 billion, reports Reuters. The deal includes USD150 million of cash from Collective Growth and USD200 million of financing from private investors including Magna International, Antara Capital, and Phoenix Insurance. As part of the agreement, the combined company will retain the name Innoviz Technologies Ltd. and will be listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the ticker symbol INVZ. The deal is expected to be closed in the first quarter of 2021. Omer Keilaf, Innoviz CEO, said, "This milestone is pivotal for our continued growth and the advancement of the autonomous vehicle industry as a whole. It requires significant investment of time and resources and we've made great strides due to the support of our investors and partners. The public listing is a major step on our path to becoming one of the dominant players in the global autonomous driving industry." (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- South Africa's real retail trade sales, seasonally adjusted,
fell by 0.2% during October. The outlook for the results in
November and December seems less optimistic. (IHS Markit Economist
Thea Fourie)
- Real retail trade sales, seasonally adjusted, dropped 0.2% month on month in South Africa during October, which follows a sharp rebound in month-on-month sales since May. South Africa's real retail trade sales, seasonally adjusted, remain below pre-COVID-19 levels and fell by 3.3% year on year (y/y) during October. During January-October, real retail sales fell by 8.4% y/y, from a growth rate of 1.4% for the same period last year.
- Most sub-components in overall retail trade sales grew during October, except for pharmaceuticals and medical goods, cosmetics, and toiletries (down by 5.4% y/y) and other retailers (down by 25.0% y/y).
- Sub-sectors that showed the strongest gains compared with a year earlier include household furniture, and appliances and equipment (up 6.4% y/y) and hardware, paint, and glass (up 5.7% y/y).
- Home working due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on local mobility has supported retail trade sales in the household furniture and appliances and equipment sub-components of total retail trade sales, as individuals renovate their working space to allow for a more-productive home office environment. This, combined with historical low interest rates in the South African economy, has meant resilience of housing sales and housing renovations, as shown in the growth in the hardware, paint, and glass sub-category. Mortgage advances by monetary institutions held up during the first 10 months of 2020, although the annual growth rate moderated somewhat from 6.2% y/y in January to 4.4% y/y in October.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Mainland China +0.7%, Japan/India/Australia +0.3%, South Korea -0.3%, and Hong Kong -0.4%.
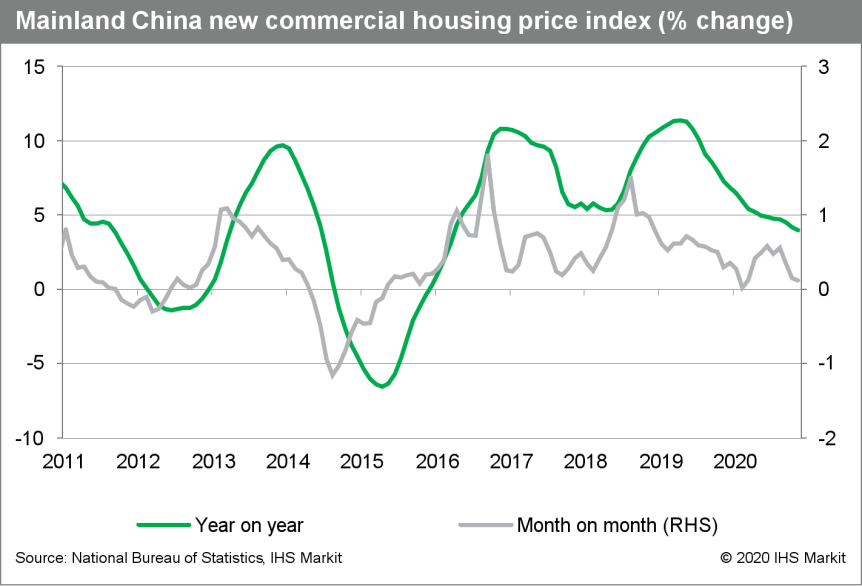
- Mainland China's new home price inflation averaged 0.12% month
on month (m/m) in November, down 0.03 percentage point from the
October reading, according a survey of 70 major cities conducted by
the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). (IHS Markit Economist Lei
Yi)
- The latest release marks the third consecutive month of decline in average month-on-month new home price inflation. In November, tier-1 cities led month-on-month disinflation across city tiers, with the reading falling 0.1 percentage point from October. Notably, new home prices in Beijing declined 0.1% m/m, while Guangzhou home prices increased 0.9% m/m, with Shanghai and Shenzhen registering no change in home prices from the preceding month.
- Up to 36 out of the 70 surveyed cities registered month-on-month new home price gains in November, compared with 45 cities in October. The number of cities reporting month-on-month price declines reached 28, the highest number since the end of 2015.
- Year-on-year (y/y) new home price inflation edged down to 4.0% in November, a low last seen in 2016. The disinflation was evenly distributed across city tiers, with each tier recording a decline of around 0.2 percentage point compared with month-ago figures. As of November, year-on-year price inflation has either declined or stayed unchanged for 19 and 20 consecutive months in tier-2 cities and tier-3 cities, respectively.
- Strength in housing sales and construction suggests continued stability in the housing market, which poses growth tailwinds for the mainland China's sustained economic recovery. Notably, housing inventory had declined for eight consecutive months as at October.
- Nevertheless, nationwide weak home price inflation is expected
to persist through 2021 as the government is increasing scrutiny on
financing of developers and buyers to curb any potential financial
risks. On 30 November, the chairman of the China Banking and
Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) openly stated that the
property market is mainland China's biggest "grey rhino" in terms
of financial risks. Further, the recent increase in bond defaults
exemplifies how economic slowdown could drive corporate failures,
despite initial mitigation by policy support.
- Mainland China's December Politburo meeting confirmed its
achievement made in the COVID-19 battle this year and targeted
stable growth through reforms in the first year of the 14th
five-year plan (FYP). (IHS Markit Economist Yating Xu)
- Mainland China will continue to focus on high-quality development with targeted macroeconomic policies to keep economic growth within a reasonable range in 2021, according to the Politburo meeting of the Communist Party presided by Xi Jinping on 11 December.
- Besides ongoing supply-side structural reforms, the meeting pointed out demand-side reforms for the first time and vowed to provide stronger support for technology innovation. Also, the meeting stressed to step up anti-monopoly efforts and prevent the disorderly expansion of capital to ensure the health development of the market.
- Demand-side reforms are in line with the strategy of expanding domestic demand and establishing domestic circulation, which was pointed out in the 14th FYP. Future policies are expected to focus on consumption upgrading and service consumption as stated by vice president Liu He. Also, expanding the range of investment and optimizing investment structure are crucial to supply reforms.
- The emphasis on capital expansion reflected government's efforts to promote fair competition and market's function in resource allocation, which will help boost technology innovation and market vitality. More actions on anti-monopoly are expected in the coming year, particularly for some new businesses. China's General Administration of Market Regulation released in November a draft guideline of anti-monopoly on platform economy.
- The December Politburo meeting is a likely prelude to the Central Economic Work Conference, which usually takes place in December and is expected to give further details about 2021 and the five-year economic development plans.
- The Chinese clothing maker that controls brands including The Lycra Company and Gieves & Hawkes revealed on Monday that it had failed to pay back investors on a $153 million bond, the latest in a string of defaults in the country. Shandong Ruyi Technology Group, which has struggled to cope with a heavy debt load after a series of high-profile international acquisitions, said in a filing that it had failed to repay the principal and interest on a Rmb1bn bond that came due on Monday. It has joined a growing list of defaults among troubled companies that have sent tremors through China's $4tn corporate bond market since November. (FT)
- McCain Foods will spend USD200 million on a second potato processing plant in China, to meet the growing demand for its potato products in Asia. The factory is to be built in the Yangling Agriculture Hi-Tech Development Zone, Shaanxi Province. It is McCain's second processing plant in the country, after the existing production facility in Harbin, Heilongjiang province. According to the USDA projections, demand for frozen French fries in China will increase "at a moderate pace over the long run" as a result of the urbanization and the increasing number of fast-food restaurants. At the same time, Chinese potato production is not efficient enough to guarantee all-year-around supply for the domestic market. Potato processing facilities run four to six months a year due to the limited supply of suitable domestic fresh potatoes and inadequate or outdated storage facilities, which lead to significant storage losses. The US is China's main supplier, but its market share fell from 66% in 2016/17 to 44% in 2019/20 on price competition from European exporters following the application of retaliatory tariffs on US products. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Cristina Nanni)
- The auto market of mainland China expanded eight months straight in November, thanks to buoyant SUV and commercial vehicle sales. According to data released by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), new vehicle sales on a wholesale basis increased by 12.6% year on year (y/y) to 2.77 million units in China during last month, while production rose by 9.6% y/y to 2.85 million units. In the near term, the COVID-19 pandemic will still bring uncertainties to auto production. The recent microchip shortage, which, in part, was caused by a resurgence of COVID-19 cases in Europe, is one factor that may impact negatively on the production of some OEMs in January 2021. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- An automobile manufacturing base in East China has started production of 5G-based driverless new energy cars, reports China Daily. The facility is established in Jinan, the capital of Shandong province, and has a construction area of about 130,000 square meters. The facility is built by China Construction Electric Power Construction Co. Ltd. and involves investment from Allcheer Intelligent Automobile. The report says the manufacturing base in its first phase can produce 100,000 smart new energy vehicles (NEVs) a year. The Chinese government is strongly prioritizing the electrification and autonomous vehicle (AV) sectors for it to gain the leadership position in the global automotive industry. For NEVs to achieve a market share of 20% by 2025, China will need to step up policy support to address bottlenecks that constrain their adoption. According to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), in the first nine months of 2020, around 734,000 NEVs were sold in China, accounting for 4.3% of total vehicle sales. Meanwhile, China is pushing to commercialize autonomous smart vehicles, which is a key part of the country's 'Made in China 2025' plan. Recently, the country released the Technology Roadmap for Intelligent-Connected Vehicles 2.0 which expects vehicles with partial autonomous functions to account for 50% of new vehicle sales by 2025. Under this plan, new vehicles with Level 2 or Level 3 automation will represent 70% of new vehicle sales by 2030. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Wuhan has built China's first autonomous vehicle (AV) technology themed park. The Longlingshan Ecological Park will deploy autonomous technology in 19 vehicles including buses, roving vending machines and cleaning vehicles. The park will open for visitors on 1 January 2021, reports South China Morning Post. The park will feature Dongfeng's autonomous tour bus for sightseers, and is designed for fixed routes within an enclosed or semi-closed area. The bus has two rows of seats with no driver's cab or steering wheel and can detect obstacles up to 15 meters away. Autonomous cleaners integrated with DeepBlue technology will carry two large sweepers in the front and a garbage box in the back. Neolix will deploy autonomous vending machines that will sell water and snacks to visitors. China is pushing to commercialize autonomous smart vehicles, which is a key part of the country's 'Made in China 2025' plan. In February, 11 Chinese central government departments jointly issued the 'Strategy for Innovation and Development of Intelligent Vehicles', with a vision to develop AVs. The strategy aims to develop an ecosystem for AVs and to have conditional AVs (Level 3) in large scale production by 2025. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Chinese auto startup Li Auto is conducting research on pure electric vehicles (EVs). According to China Daily, Li Auto aims to produce battery electric vehicles (BEVs) based on the next generation of electric technologies, which are expected to include super-fast charging technology, high-voltage charging platforms and high-charging-rate batteries. However, the company said there is no timetable for when its first BEV project will begin. Li Auto is currently the only startup in the Chinese market that offers an extended-range EV. Li Auto's November sales report indicates that it delivered 3,692 vehicle during the month, setting a new record for its monthly deliveries since January. In the next three years, the startup is likely to stay focused on its extended-range EV product line-up, which will expand from the Li One to a range of mid-to-full-size sport utility vehicles (SUVs) positioned in the premium market. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ)'s December Tankan diffusion index (DI)
of current business conditions for large manufacturing groupings in
BoJ's December Tankan survey moved up 17 points to -10. The largest
improvement since the second-quarter 2013 survey reflected the
resumption of business activity in Japan and the country's trade
partners, and was driven by improvements in the DIs for a broad
range of industry groupings, particularly motor vehicles, iron and
steel, non-ferrous metals, and production machinery. However, only
the DI of food and beverages turned to positive territory (moving
up seven points to 5). (IHS Markit Economist Harumi Taguchi)
- The DI for large non-manufacturing groupings also moved up seven points to -5. The DI for communication, information services, and retailing continued to rise, reflecting stay-at-home/working-from-home lifestyles. The DIs for accommodation, eating, and drinking services (up 21 points to -66), services for individuals (up 22 points to -38), and transport and postal activities (up 14 points to -24) improved substantially but remain far below zero. The DIs for small manufacturing and non-manufacturing enterprises also improved by 17 points to -27 and 10 points to -12, respectively.
- The DIs for domestic and overseas supply and demand conditions suggested that the solid improvement in business conditions for manufacturing was thanks to domestic and external demand and supply conditions. However, domestic demand and supply conditions for non-manufacturing remained weak.
- Downbeat outlooks lead to downward revisions for sales and profit outlooks
- The forecast DI for three months out showed narrower contractions for large and small manufacturing groupings (up 2 points to -8 and up 1 point to -26, respectively), reflecting expectations for continued improvement for domestic and overseas demand and supply conditions. However, the forecast DI for large non-manufacturing groupings dropped one point to -6 and the forecast DI for small non-manufacturing groupings fell by 8 points to -20, reflecting expectations for weaker demand, which was probably because of concerns about the resurgence of COVID-19 and the suspension of government travel and other subsidies for high-infection areas.
- The December 2020 figures suggest that business conditions have improved, but recovery is still patchy and upward momentum could weaken because of the resurgence of COVID-19. The au Jibun Bank Purchasing Managers' Index (calculated by IHS Markit) signaled that the business conditions are close to neutral for manufacturing (49.0 in November) and services (business activity index at 47.8 in November). While this partly reflects differences in methodology and the sample base, guidelines for reducing the operation hours of drinking places in a larger number of prefectures and an ongoing uptrend in new confirmed COVID-19 cases could weigh on business confidence. The sluggish results could prompt the government and BoJ to consider extending the duration of measures to support businesses and special lending programs.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-december-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-december-2020.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+December+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-december-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 14 December 2020 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-december-2020.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+14+December+2020+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-14-december-2020.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




