Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jun 10, 2020
Export hub status of Hong Kong endangered by the US-China trade war?
Key points:
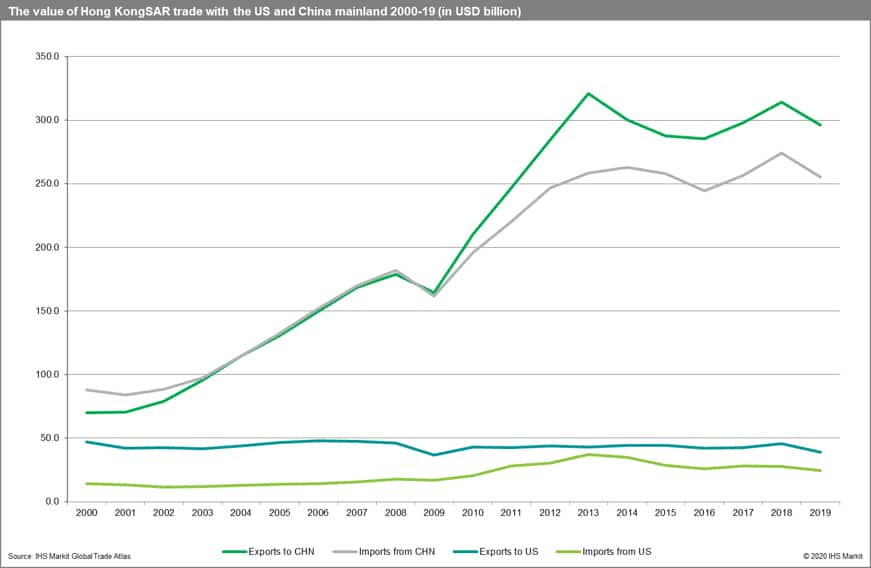
- The value of Hong Kong SAR exports to China mainland went up from USD 69.9 billion in 2000 to 296.1 billion in 2019 (with a CAGR of 7.9%). The highest value of exports was reached in 2013 (USD 320.8 billion). The value of imports went up from USD 87.8 billion in 2000 to 274.4 billion in 2019 (with a CAGR of 5.8%).
- The value of Hong Kong SAR exports to the United States went down from USD 47.0 billion in 2000 to 39.1 billion in 2019 (with CAGR of -1.0%). The highest value of exports was reached in 2006 (USD 47.8 billion). The value of imports from the US went up from USD 14.4 billion in 2000 to 24.6 billion in 2019 (with CAGR of +2.8%).
- Most of the Hongkongese exports to the US are re-exports (depending on a year they accounted from 85.1% up to 99% of total exports). Since 2013 the share of domestically produced goods in this trade stream is less than 2% (1.2 % in 2019).
- Within the re-exports, the re-exports from China mainland clearly dominate (they account from 76.8% to 88.8% of the value of total exports to the US). The share of re-exports from China is steadily falling since 2009.
- In value terms, re-exports from China going through Hong Kong SAR to the US increased from USD 36.5 billion in 2000 to 40.4 billion in 2007. In 2019 they were equal to USD 30.0 billion only.
- The share of re-exports by Hong Kong SAR of Chinese-origin goods in total American imports (taking the direct and indirect route through Hong Kong) from China mainland is falling. Hong Kong SAR was responsible for 26.9% of the trade in 2000. It went down to 13.7% in 2005 and reached 6.3% in 2019.
- At the commodity HS 6-digit level of disaggregation, we can identify a number of electronic goods (smartphones, computers, and their parts, cameras, printed circuits, semiconductors, headphones, etc.), jewelry, and apparel as the main re-exported Chinese goods going through Hong Kong to the US.
- The high-tech goods can be particularly susceptible to potential sanctions on the so-called dual-use goods if the United States decided to impose sanctions under the legislation in force.
- The share of re-exports from Hong Kong SAR in total direct and indirect imports of the US from China mainland went down to 5.7% and reached 4.6 billion USD in the Q1 of 2020. If this continues through the remainder of 2020, the value of re-exports to the US of Chinese-origin goods can go down by even as high as 40%.
Trade relations of Hong Kong with China mainland and the United States 2000-19
Using the Global Trade Atlas from the IHS Markit Maritime & Trade division we are able to have a closer look at the trade relations between Hong Kong SAR, China mainland, and the US.
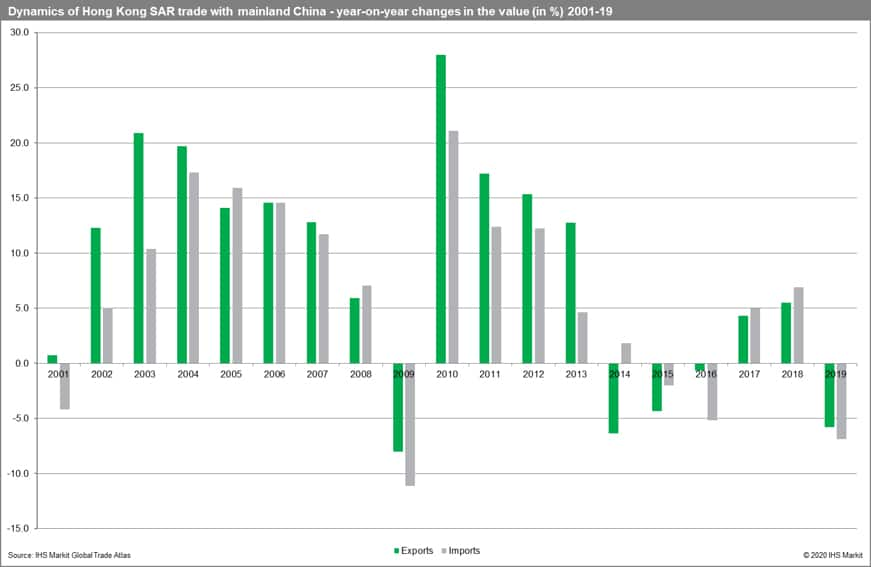
The value of Hong Kong SAR exports to China mainland went up from USD 69.9 billion in 2000 to 296.1 billion in 2019 (with a CAGR of 7.9%). The highest value of exports was reached in 2013 (USD 320.8 billion). The value of imports went up from USD 87.8 billion in 2000 to 274.4 billion in 2019 (with a CAGR of 5.8%). Since 2009 Hong Kong SAR has a permanent trade surplus in its relations with China mainland.
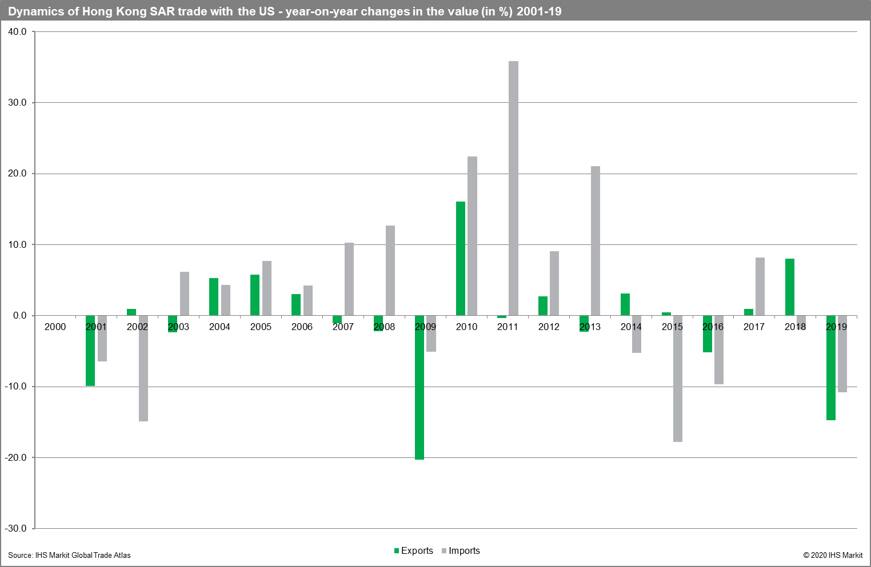
It is important to stress that China mainland is a significantly more important trade partner of Hong Kong SAR than the US. The value of Hong Kong SAR exports to the United States went down from USD 47.0 billion in 2000 to 39.1 billion in 2019 (with CAGR of -1.0%). The highest value of exports was reached in 2006 (USD 47.8 billion). The value of imports from the US went up from USD 14.4 billion in 2000 to 24.6 billion in 2019 (with CAGR of +2.8%). Imports from the US reached their maximum in 2013 (USD 37.0 billion). Throughout the whole analyzed period (2000-19) Hong Kong SAR has enjoyed a permanent trade surplus in its relations with the US.
The value of trade with both trade partners as well as its dynamics are presented in the following charts.
Hong Kong as one the biggest re-exporter hubs in the world
In our analysis, we have to take into account that Hong Kong SAR is one of the world's biggest re-exporter and serves as an intermediator in trade relations between China mainland and the US. This position is based to a large extent on its privileged status in trade relations with the US vis-à-vis China mainland.
If we look deeper into the structure of the Hongkongese trade with the US, we see that most of the exports are re-exports (depending on a year it accounted from 85.1% up to 99% of total exports). Since 2013 the share of domestically produced goods is less than 2% (1.2 % in 2019). Within the re-exports, the re-exports from China mainland clearly dominate (they account from 76.8% in 2019 to 88.8% of the value of total exports). It is important to stress that the share of re-exports from China is steadily falling since 2009.
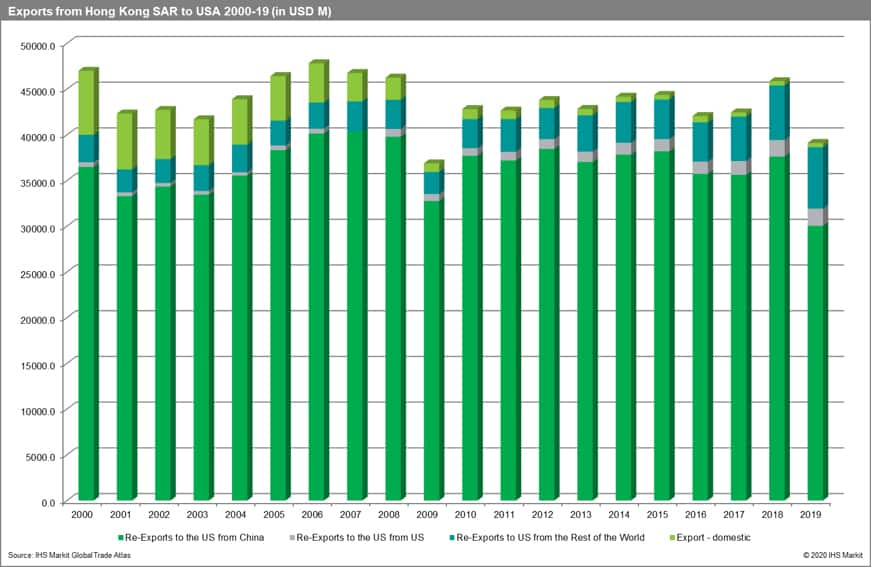
In value terms, the value of re-exports from China going through Hong Kong SAR increased from USD 36.5 billion in 2000 to 40.4 billion in 2007. It was significantly affected by the global financial crisis and then rebounded and reached approx. USD 38.0 billion in the period 2007-2015. It went down in 2016-2017, rebounded in 2018, and then collapsed to USD 30.0 billion possibly due to rising tensions in the trade war between the United States and China mainland.
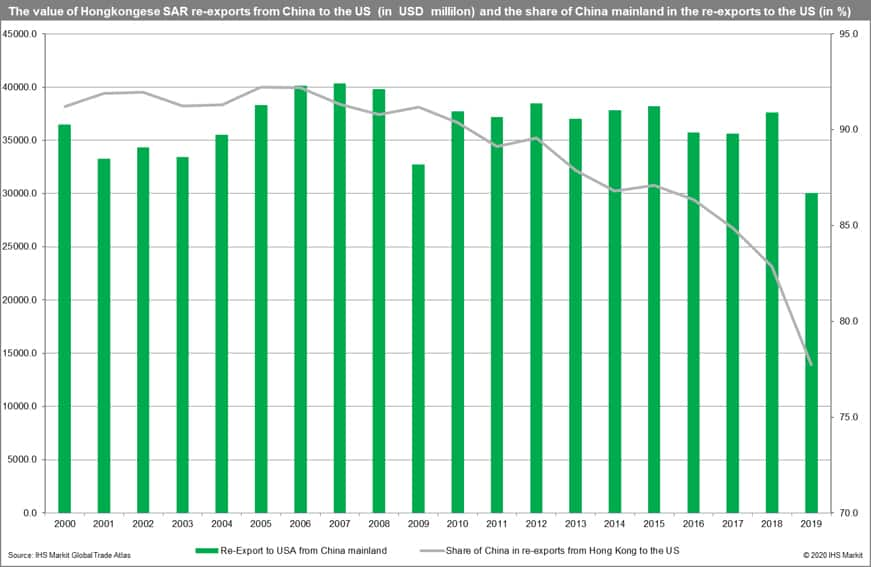
The role of Hong Kong in total US imports from China mainland
If we think of US imports from China mainland we can see that part of them go indirectly by Hong Kong SAR. Thus in the following, the total imports from China mainland are treated as direct imports from China mainland as well as the re-exports by Hong Kong SAR of Chinese-origin goods.
The share of re-exports by Hong Kong SAR of Chinese-origin in total American imports from China mainland is falling. Hong Kong SAR was responsible for 26.9% of the trade in 2000. It went down to 13.7% in 2005 and reached 6.3% only in 2019.
It is interesting to see the structure of total American imports from China mainland taking the above definition into account. Analyzing the structure of trade at the 2-digit level of commodity disaggregation of HS we are able to identify a number of commodity groups with high significance. The highest share of re-exports from China mainland applies to clocks and watches as well as pearls (HS 91) - 45.1%, metal-clad metals and imitation jewelry (HS71) - 35.4% as well tin articles from the tin (HS 80) - 35.2%.

Source: IHS Markit Global Trade Atlas
We can also look at the data from the point of view of the value of the re-exports. Looking at the data from this perspective we can easily identify the most important 2-digit commodity groups. These are electrical machinery and equipment and parts (HS 85) - USD 13.1 billion, nuclear reactors, boilers, machinery and mechanical appliances (HS84) - USD 4.3 billion as well as articles of apparel and clothing accessories, not knitted or crocheted (HS62 ) - USD 2.0 billion and articles of apparel and clothing accessories, knitted or crocheted (HS 61) - USD 1.8 billion.

Source: IHS Markit Global Trade Atlas
In order to identify the most important commodity groups trade, it is worthwhile to perform the analysis at a deeper level of disaggregation. We have performed it at HS 6 level.
The following tables provide the top 22 commodity groups at HS 6-digit levels accounting for 50% of the value of re-exports from Hong Kong SAR of Chinese-origin goods to the US. At this level of disaggregation, we can identify electronic goods (smartphones, computers, and their parts, cameras, printed circuits, semiconductors, headphones, etc.), jewelry, and apparel as the main re-exported goods. The high-tech goods can be particularly susceptible to potential sanctions on the so-called dual-use goods if the United States decided to impose sanctions under the legislation in force.
We have been able in addition to identify a large group of HS 6-digit commodities (462 goods) imported to the US only indirectly through Hong Kong SAR. In total they, however, add up only to USD 1.5 million - so are of residual value. Besides we identify a group of 1903 commodities which are mostly (share of 50.0% or above, below 100%) imported from China indirectly through Hong Kong SAR. These add up to USD 15.15 billion (with top 112 commodity groups accounting for USD 10.0 billion).
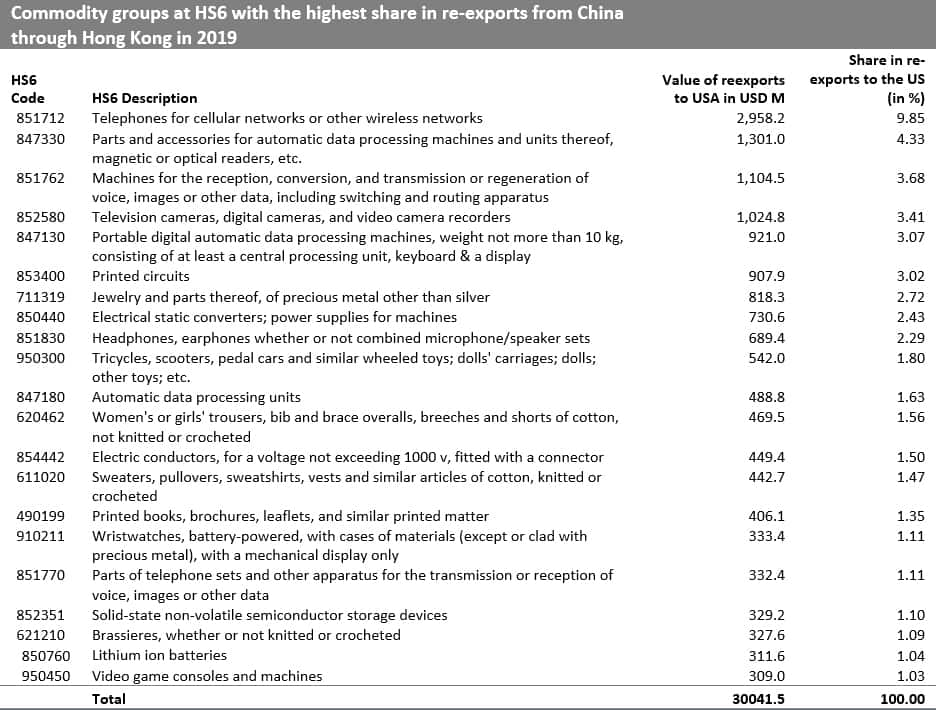
Source: IHS Markit Global Trade Atlas
The situation in Q1 2020
We have furthermore performed the analysis for the Q1 2020. The share of re-exports from Hong Kong SAR in total direct and indirect imports of the US from China mainland went down to 5.7% and reached 4.6 billion USD. Taking the current situation into account it is difficult to predict its total value in 2020 - it is very likely to be significantly lower than in 2019 (it could be lower even by 40% if we assume the Q1 2020 readouts as a good predictor for the whole year).
This column is based on data from IHS Markit Maritime & Trade Global Trade Atlas main and the EDF modules.
The background
Hong Kong SAR is a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China situated in the eastern Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. It used to be a British colony until 1997 when it was transferred back to China mainland as a special administrative region. Hong Kong is highly autonomous with its governing and economic systems independent from that of mainland China under a principle of "one country, two systems". The terms of the Sino-British Joint Declaration and Hong Kong's Basic Law state that this special status is supposed to be protected until 2047.
As a highly autonomous territory, with a separate legal system as well as currency and customs jurisdiction, Hong Kong SAR provides numerous business opportunities for foreign companies, which include:
- No customs tariff and limited excise duties,
- Strong rule of law and respect for property rights,
- Open system for transferring money and other trade relations not subject to strict Chinese currency exchange regulations,
- Expertise in finance and marketing, sophisticated infrastructure, and access to mainland China's manufacturing base.
Moreover, Hong Kong SAR is a part of the Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement (CEPA) which is an economic and trade agreement between the separate customs territories within the People's Republic of China. This agreement provides preferential access to the China mainland's market for Hong Kong's products and companies. CEPA goes even beyond China's World Trade Organization (WTO) commitments and eliminates tariffs and allows earlier or preferential access to some services sectors. This is also beneficial for overseas companies and foreign investors, who are allowed to set up production lines in Hong Kong to produce goods that meet the CEPA rules of origin requirements.
Not only Chinese businesses, but also the US has benefited from Hong Kong's special status and they both contributed to Hong Kong SAR becoming a global financial and trade hub. Hong Kong SAR is a strategic location for US companies, doing business in the region, especially small and medium-sized firms. Around 1,300 US companies are operating in the city of Hong Kong alone.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fexport-hub-status-of-hong-kong-endangered-by-us-china-trade-war.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fexport-hub-status-of-hong-kong-endangered-by-us-china-trade-war.html&text=Export+hub+status+of+Hong+Kong+endangered+by+the+US-China+trade+war%3f+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fexport-hub-status-of-hong-kong-endangered-by-us-china-trade-war.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Export hub status of Hong Kong endangered by the US-China trade war? | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fexport-hub-status-of-hong-kong-endangered-by-us-china-trade-war.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Export+hub+status+of+Hong+Kong+endangered+by+the+US-China+trade+war%3f+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fexport-hub-status-of-hong-kong-endangered-by-us-china-trade-war.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




