Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
ECONOMICS COMMENTARY
Nov 19, 2025
Assessing the relationship between the PMI and official statistics in Malaysia
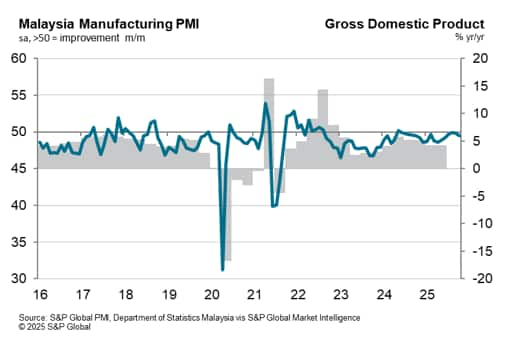
PMI data are available faster and more frequently than official GDP and industrial production figures, providing an accurate and timely advance guide to economic growth in Malaysia.
To estimate PMI-implied GDP growth rates, we can build a simple OLS regression model where:
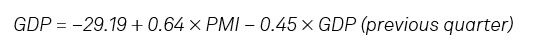
This formula states that for every one-point increase in the PMI Output Index over a calendar quarter, there is approximately a 0.64-point rise in GDP for the corresponding quarter. The positive coefficient indicates a strong relationship between the Output Index and GDP, suggesting that as the manufacturing output expands - as indicated by a rising PMI reading - the overall economy grows.
A PMI reading of 45.5 is therefore consistent with no year-on-year growth in the broader economy as measured by GDP.
A p-value below the conventional 0.05 threshold further underscores this relationship as statistically significant, meaning that we can be confident that this relationship is not due to random chance, and that the PMI is a meaningful pulse-check on the Malaysian economy.
Growth in the previous quarter has an impact on GDP
This analysis also investigated the impact of GDP in the prior period on growth in the Malaysian economy. It found a negative coefficient of approximately -0.45. This figure suggests that higher GDP in the previous period is associated with a slight decrease in current growth, suggesting that the economy may have a tendency of natural adjustment or correction phase after a period of growth.
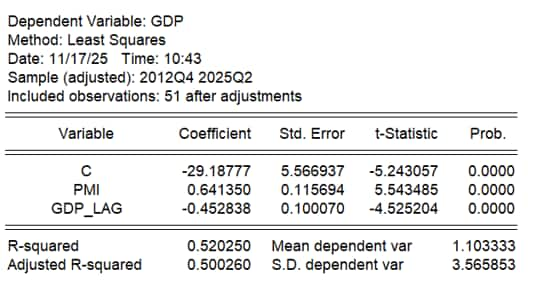
Accuracy
Assessing the feasibility of this model, we can look into several results from the regression. The R-squared figure came in at 0.52, suggesting around 52% of the variability in GDP can be explained by the model. While this suggests that there are other factors influencing GDP not captured in this analysis, the model still provides a reasonable explanation of the relationship between PMI and GDP.
The overall F-statistic of 26.03 indicates that the model as a whole is statistically significant. This suggests that the included variables do a good job of explaining the variations in GDP.
The result of this regression underscores the value of the Malaysia Manufacturing PMI in tracking the health of the broader economy, and the timeliness of release provides these insights ahead of official statistics. Specifically, for every one-point increase in the PMI, GDP tends to increase by approximately 1.12 points. This suggests a strong positive relationship; when manufacturing activity is robust, it often signals a growing economy.
However, the results also highlighted the importance of lagged GDP-essentially, how past GDP performance impacts current figures. A decrease in previous GDP levels tends to drag down current GDP, indicating that economic recovery takes time.
Signals
In summary, a thriving manufacturing sector will typically boost GDP, though past economic performance also plays a crucial role. If Malaysia's PMI is trending upward, the model suggests a lift in GDP growth is likely to follow.
Conversely, persistent PMI weakness would be a warning sign of broader cooling in economic activity. Furthermore, the negative coefficient for lagged GDP hints at the likelihood that strong growth in one quarter tends to be followed by a partial cooling in the next and vice versa, which could dampen the signal from a strong PMI that quarter.
Current assessment
Latest data from the Malaysia Manufacturing PMI pointed to challenging conditions for the sector at the start of the fourth quarter of 2025. Firms recorded a renewed reduction in new orders, which contributed to a sustained scaling back of production volumes. Muted conditions also fed into firms' decisions on employment and stock holdings, all of which moderated during October. Though the October data was less positive, the relationship between the PMI and official statistics suggests that both GDP and manufacturing production continued to rise into the final quarter. Taking the above formula, with an average third quarter reading for the PMI Output Index of 49.6 and second-quarter GDP growth coming in at 2.12%, the model suggests that GDP can be expected to grow approximately 1.6% in the third quarter of 2025.
Encouragingly, manufacturers cited stronger optimism regarding the outlook for the year ahead. Positive sentiment reached a two-and-a-half year high amid hopes that new orders will increase.
The November S&P Global Malaysia Manufacturing PMI is due to be published on 3rd December and will provide further insights and indicators into the health of the manufacturing economy and overall economic growth as 2025 nears its end.
Usamah Bhatti, Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
Tel: +44 1344 328 370
usamah.bhatti@spglobal.com
© 2025, S&P Global. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole
or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI®) data are compiled by S&P Global for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fassessing-the-relationship-between-the-pmi-and-official-statistics-in-malaysia-nov25.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fassessing-the-relationship-between-the-pmi-and-official-statistics-in-malaysia-nov25.html&text=Assessing+the+relationship+between+the+PMI+and+official+statistics+in+Malaysia+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fassessing-the-relationship-between-the-pmi-and-official-statistics-in-malaysia-nov25.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Assessing the relationship between the PMI and official statistics in Malaysia | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fassessing-the-relationship-between-the-pmi-and-official-statistics-in-malaysia-nov25.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Assessing+the+relationship+between+the+PMI+and+official+statistics+in+Malaysia+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fprod.azure.ihsmarkit.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fassessing-the-relationship-between-the-pmi-and-official-statistics-in-malaysia-nov25.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}




