Published February 2022
Synthetic zeolites account for 63% of total zeolites consumption; natural zeolites account for the remainder. Synthetic zeolites are used mainly as detergent builders, catalysts, and absorbents/desiccants, while natural zeolites are used for feed additives, soil amendment, water treatment, environmental uses, and construction. The largest-volume use for synthetic zeolites is as a builder in home laundry detergent, accounting for 62% of the total. Catalysts, primarily fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts, are the second-largest synthetic zeolite use, with about 20% of the total volume. Consumption for adsorbent/desiccant applications accounts for the smallest share, but will be the fastest-growing market, driven by the recovery of construction markets (use as a desiccant in insulated multiglazed windows), the natural gas market (as a drying agent), and environmental applications (trapping volatile organic compounds [VOCs] to prevent release into the environment).
Zeolites have been the beneficiaries of growing public sensitivity to environmental issues. As aluminosilicates, they have generally been accepted as harmless replacements for more environmentally damaging products. The environmental impact of zeolites has been fully characterized by life cycle analysis.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of zeolites:
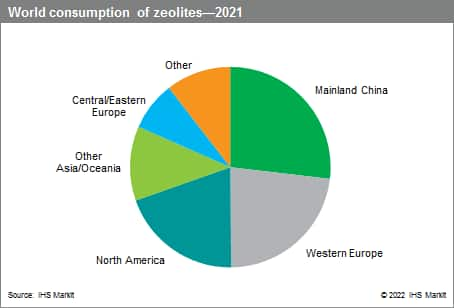
The largest-volume use for synthetic zeolites is as a builder in home laundry detergent powders. In developed countries (North America, Western Europe, and Japan), the use of detergent zeolites is mature and has shown a declining trend. The decline is due to the increased efficiency of the zeolite builders, competition from other builders, and increased use of liquid detergents that do not contain zeolites.
The second-largest synthetic zeolite use is for the production of catalysts. These catalysts are used principally for petroleum catalytic cracking, with small volumes consumed in hydrocracking and chemical synthesis. North America is the largest market for zeolite catalysts. Mainland China is the second-largest market. Overall growth for this market is expected to be about 1–2% per year through the forecast period.
Global demand for fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts and automotive/transportation fuels, largely in developing Asian countries and the Middle East, continues to rise. Synthetic zeolites are a key ingredient in catalysts used for FCC. The declining crude oil quality and the rising air pollution standards have opened up opportunities for zeolite manufacturers in FCC catalysts market. However, this market is difficult to penetrate as it is largely dominated by three major global companies.
The third major end use for synthetic zeolites is adsorbent/desiccant applications. Demand in this application has shown some overall growth mainly as a result of an increase in environmental projects such as reduction of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Future demand growth should be slow in developed regions, and fast in developing countries.
Globally, demand for synthetic zeolites is expected to increase only slowly, at an average annual rate of about 0.8%.
Natural zeolites include minerals capable of ion exchange, such as clinoptilolite, chabazite, and mordenite. Mainland China is the largest producer of natural zeolites, followed by South Korea and Slovakia. Other than the large volumes in these countries, world production is highly decentralized. The largest end use for natural zeolites is as a cement additive to produce a slower-hardening and stronger product. Other major end uses are as a nutrient-release agent in soil conditioners, in animal feeds, and as an odor control agent in animal litter.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook - Zeolites is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Zeolites has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers, organizations and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence, expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you:
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















