Published July 2022
From 2007 to 2012, consumption of urethane coatings dropped in North America, Western Europe, and Japan, but was offset by growth in mainland China and other developing economies. There was good consumption growth in 2012–18 in all regions, followed by some contraction in 2020–21 because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Future consumption growth for urethane coatings will likely be about 2–3% per year. The majority of consumption growth will take place in Asia Pacific, Africa, and the Middle East, with lesser growth in the mature North American, Western European, and Japanese markets.
Urethane coatings have been one of the fastest-growing sectors of the worldwide paint and coatings industry. Despite the relatively high cost, their excellent durability, resistance to corrosion and abrasion, pleasing optical properties, and flexibility make urethane coatings suitable for a range of high-performance applications. Urethanes are also finding greater appeal in recent years because of the ability to formulate coatings with lower organic solvent contents.
Polyurethane surface coatings, often referred to as urethane coatings, are high-cost, high-performance coatings that are noted for low-temperature curing, high flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, and good outdoor weathering characteristics. Typical uses for these coatings are on wood furniture; floors; automobiles, aircraft, and other vehicles; machinery and equipment; electrical goods; and industrial structures.
Urethane coatings can be made from a wide range of raw materials, and can be easily modified to enhance certain properties such as ultraviolet (UV) resistance, hardness, flexibility, chemical resistance, and others. One of the main differentiations in raw materials is the type of isocyanate used, where aliphatics (mainly HDI, IPDI, and H12MDI) are used in applications that must withstand exposure to UV light, while less-expensive aromatics (mainly TDI and MDI) are used for primers and wood coatings, where yellowing is acceptable. In addition, a variety of coating technologies are available, including solventborne, waterborne, powder, and UV curable. Waterborne technology in particular has grown rapidly in the last few decades for finishing wood, textiles, plastics, and metals.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of polyols and isocyanates for urethane surface coatings:
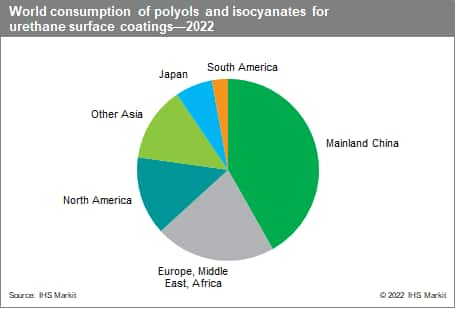
Certain markets are dominant in all three industrialized regions, including automotive refinishes, wood finishes, and high-performance anticorrosive coatings. The fastest-growing market for urethanes in the 1990s was automotive OEM clear coat finishes; penetration has slowed in recent years. Urethane clear coats now account for 25% of the topcoat market in Europe and 14% in North America. In Japan, only small amounts of urethane formulations are now used for topcoats. In Europe, wood product finishing is much more important than in the United States, but urethane powder coatings are more significant in the United States. In all regions, urethane coatings are used in premium vehicle refinishes.
Mainland China now accounts for 42% of the global market for urethane coatings. The fastest-growing application has been for automotive refinishing applications, a result of increasing automobile ownership and much higher accident rates in the country.
The urethane coatings industry consists of resin manufacturers and coatings formulators. There is little integration, except in the automotive OEM and refinish coatings businesses, where PPG, BASF, Axalta, and others can make polyols for captive use. Except for isocyanates, most raw materials for urethane coatings are fairly easy to make and do not require large capital investments. The major worldwide producer of isocyanates for coatings is Covestro, which sells a complete line of aliphatic (UV light stable) and aromatic isocyanates to formulators around the world from plants in North America, Europe, and Asia. Other suppliers of isocyanates for coatings include Vencorex (plants in Europe, North America, and Thailand), Evonik (Europe and North America), BASF (Europe and mainland China), Asahi Kasei (Japan and mainland China), Tosoh (formerly Nippon Polyurethane) (Japan), Mitsui Chemicals (Japan), and Wanhua Chemical (formerly Yantai Wanhua) (mainland China).
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Urethane Surface Coatings is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Urethane Surface Coatings has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















