Published September 2023
Urea is the most popular form of solid nitrogen fertilizer, particularly in the developing regions of the world, and is traded widely on the international market. Urea prices can fluctuate markedly and frequently, depending on crop prices, which affect demand. Around 80%-85% of the production is used as a fertilizer. Urea is also used increasingly in the industrial sector to make urea-formaldehyde resins, melamine, diesel exhaust fluids (DEF) and livestock feeds. It is also used to make adhesives and paints, laminates, molding compounds, paper and textiles.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of urea:
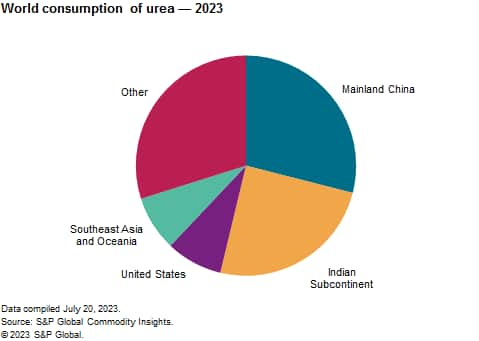
Growth in the consumption of urea is driven, in part, by the increasing global population, available disposable income, and dietary changes. In addition, although arable land has been increasing, the amount of arable land per capita has been decreasing as a result of the increases in population. As a result, more fertilizer will be needed to meet the growing need for food.
Demand originating from the nonfertilizer sector is seen to have a growing potential for urea, mostly in deNOx applications in North America, Europe and East Asia. Use in environmental applications is significant and growing rapidly for both mobile and stationary nitrous oxide (NOx) reduction, which is being mandated by legislation. Urea is used as a diesel exhaust fluid as one of the key elements of the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) process to reduce nitrous oxides from heavy-duty diesel engines.
Fertilizer applications accounted for a majority of all urea consumption in 2023. Industrial applications accounted for the remainder, led by production of urea-formaldehyde resins and melamine, livestock (animal) feed, and environmental and other applications.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Urea is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Urea has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations and other factors on chemical profitability


















