Published June 2023
With only five major producers worldwide, the propionic acid business can be considered a global one, with trade playing a significant role in the global supply/demand pattern. Production capacity is geographically concentrated in mainland China, Western Europe and the United States. BASF is the only western producer operating a facility in Asia via its 50% subsidiary BASF-YPC. The propionic acid business is characterized by a high level of integration and most manufacturers produce propionic acid as well as its raw materials — either ethylene or propionaldehyde, or both.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of propionic acid:
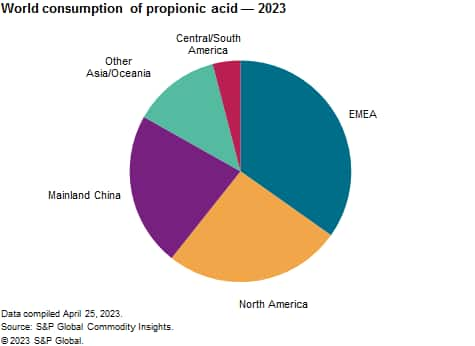
Animal feed and grain preservation accounts for slightly more than 40% of the propionic acid consumed worldwide. Propionic acid, or a buffered solution with ammonium salt, is added to animal feed to prevent the growth of mold (acquired as contaminants in the field or during storage). In general, usage depends on the moisture level of the feed, the storage time and the type of livestock, with ruminants showing a higher tolerance compared with poultry and pigs.
Another 40% of the propionic acid consumed is used in the manufacture of calcium and sodium propionates. Calcium and sodium propionates are permitted additives for both food and feed preservation. The use of calcium and sodium propionates in food is growing fast in India, mainland China, the Middle East and Africa as well as in South America. This is also driving propionic acid consumption in Western Europe, mainland China and North America, as these regions are major producers and exporters of the propionate salts.
Other significant end uses of propionic acids are in the manufacture of herbicides and diethyl ketone, while smaller-volume applications include cellulose acetate propionate, solvent esters, flavors and fragrances and plasticizers.
The global market for propionic acid has been growing at an average annual rate of around 3% during the past three years, and this is expected to continue during 2023–28. Consumption for food and feed preservatives, especially in Asia and South America, will be the major driver of this growth. In these regions, improving standards of living and the increasing popularity of processed food are supporting the use of propionate salts in food. Furthermore, increasing demand for meat in developing regions as well as the trend toward industrialized farming will also drive the use of propionic acid in feed applications.
Thanks to recent capacity expansion in mainland China, the market is presently amply supplied. This is expected to remain through 2028, as new capacity in mainland China is already on the way.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Propionic Acid is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Propionic Acid has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations and other factors on chemical profitability


















