Published December 2023
Polyvinyl acetate includes all homopolymers and copolymers where the vinyl acetate content is at least 50%. About 80% of total consumption is used in wood, construction and paper adhesives, and architectural coatings. Most of the remaining polymers are used in paper and textile coatings. Almost all of these polymers are made in emulsion form. Copolymers generally consist of 80%-90% vinyl acetate and 10%-20% butyl acrylate, ethylene, vinyl versatate or some other modifier. Generally, uses are well established, and consumption trends mirror those of GDP. In North America and Western Europe, consumption is expected to grow by 1.5%-2% per year during 2023–28. Consumption in Asia is expected to grow by 3%-4% annually.
Some polymer types have grown more rapidly than others. Copolymers of vinyl acetate–ethylene (VAE) have been growing relatively fast since they can be used in architectural coatings with very low levels of solvent (low volatile organic compounds [VOCs]). Also, consumption in construction mortars has been growing for bonding larger ceramic tiles to vertical surfaces. The product can be used in powdered form for easy transport and mixing at the construction site. The leading producers of these copolymers are Wacker, Celanese and Dairen, all of which are scheduled to add capacity in the next few years.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of polyvinyl acetate:
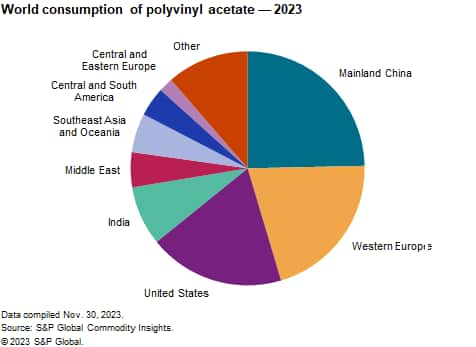
In 2023, PVAc homopolymer production in mainland China accounts for over 49% of all PVAc. The PVAc copolymers produced in mainland China are largely VAE and vinyl acetate/acrylic ester copolymers. PVAc is used for adhesives, coatings, construction and other uses. Consumption is expected to increase at about 2.9% per year through 2028.
Western European consumption of polyvinyl acetate and its copolymers is forecast to grow at 1.5% per year during the next five years. PVAc homopolymers and VAE polymers are still the dominant products used, but redispersible VAE powders will show the most growth. Adhesives and coatings applications currently dominate PVAc consumption. The most important issue facing Western European producers of PVAc and copolymers is the sourcing of vinyl acetate, the main raw material. A considerable amount of vinyl acetate capacity has recently been closed in the region, which now must import about 65% of its requirements.
In the United States, overall polyvinyl acetate consumption will continue to follow general economic growth and increase at an average annual rate of just under 2% during 2023–28. PVAc-based adhesives (primarily homopolymers and VAE copolymers) for use in packaging and construction will provide the strongest growth opportunities. In coatings, use of VAE emulsions will continue to grow as the industry continues to switch to lower-VOC-containing formulations. Other PVAc copolymers that are widely used in the coatings market, the so-called vinyl acrylics (containing 85% vinyl acetate and 15% n-butyl acrylate), have lost market share to higher-performing all-acrylic emulsions.
There are numerous producers and users of polyvinyl acetate and copolymers; many producers have annual capacities of less than 30,000 metric tons. Capacities are flexible, as producers can make other emulsion products in the same equipment. Some adhesives and coatings producers also make resin for captive use. Because polyvinyl acetate and copolymers are usually used in emulsion form with 40%-50% water content, production is generally located close to end-use industries, such as adhesive or coating manufacturing facilities and textile mills, to minimize freight costs.
This report excludes production of vinyl acetate polymers where the vinyl acetate content is less than 50%, which is chiefly in ethylene–vinyl acetate (EVA) resins, which are used in injection molding, adhesive and film applications, and are covered in the CEH Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) Resins and Vinyl Acetate reports.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Polyvinyl Acetate is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Polyvinyl Acetate has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















