Published December 2021
The ethylene-propylene elastomer market is forecast to grow at an average annual rate of more than 3.4%, driven primarily by the automotive and construction industries. The largest market will continue to be automotive components; growth will continue as the automotive industry recovers from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Consumption in automotive applications accounts for 60–65% of global demand (including use in oil additives, as well as most polymer modification uses). The major drivers of this market continue to be polymer modification, appliances parts, and the construction industry.
Ethylene-propylene elastomers are one of the largest synthetic rubbers consumed worldwide, characterized by their outstanding resistance to ozone, aging, weather, and high temperatures. Apart from that, they possess good low-temperature flexibility and have excellent electrical properties. These combined characteristics make EP elastomers particularly useful in certain automotive parts/components, single-ply roofing, appliance parts, polymer modification, wire and cable sheathing, viscosity index improvers for lubricating oils, hoses, sports fields and tracks, and other miscellaneous applications.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of ethylene-propylene elastomers:
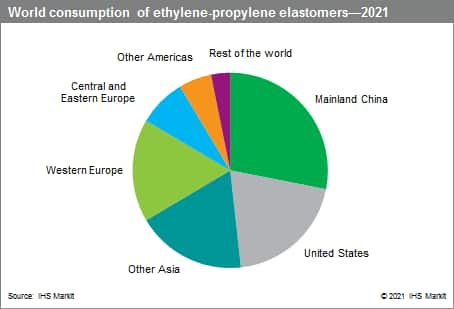
In 2021, mainland China was the largest consumer of EP elastomers, accounting for more than one-fourth of total demand, driven by the steady growth in the Chinese automotive industry in recent years. The United States is the second-largest consumer of EP elastomers. The European region as a whole is another significant market; growth in Central and Eastern Europe will outpace that in Western Europe because of the faster growth of its automotive industry. Consumption growth in Japan and South Korea will be moderate, in pace with the slow recovery of automobile production, but both will remain major exporters to other world markets. The world consumption situation for EP elastomers will be similar by 2026, as mainland China will continue to dominate the market.
As capacity for EP elastomers has increased in mainland China to meet increasing domestic demand, global utilization rates fell to only 70% in 2018. As a result, some plants in the United States and Western Europe were shut down in 2020–21, and a plant in Japan will be shut in 2023. There are still plans for additional capacity in mainland China; nevertheless, global operating rates are expected to improve to about 87% by 2026.
Future consumption of EP elastomers will depend on several important key factors—continuing competition between EP elastomers and other polymers/copolymers; automobile production levels; the level of new building construction, along with competition among single-ply roofing materials and reroofing rates; and regional GDP growth.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Ethylene-Propylene Elastomers is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Ethylene-Propylene Elastomers has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















